0000819050Q2FALSE202212/31.0222.022200008190502022-01-012022-06-3000008190502022-08-11xbrli:shares00008190502022-06-30iso4217:USD00008190502021-12-31iso4217:USDxbrli:shares0000819050us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:ProductAndServiceOtherMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RoyaltyMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RoyaltyMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RoyaltyMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RoyaltyMember2021-01-012021-06-3000008190502022-04-012022-06-3000008190502021-04-012021-06-3000008190502021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-12-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-12-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-12-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-01-012022-03-3100008190502022-01-012022-03-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-01-012022-03-3100008190502022-03-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-03-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-03-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-03-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2022-06-300000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2022-06-3000008190502020-12-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2020-12-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2020-12-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2020-12-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-01-012021-03-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-01-012021-03-3100008190502021-01-012021-03-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-01-012021-03-3100008190502021-03-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-03-310000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-03-310000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-03-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-04-012021-06-3000008190502021-06-300000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMember2021-06-300000819050us-gaap:AdditionalPaidInCapitalMember2021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RetainedEarningsMember2021-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:MilestonePaymentsMembersrt:MaximumMember2022-06-300000819050us-gaap:SubsequentEventMember2022-07-052022-07-05xbrli:purebbi:segment0000819050us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2022-06-300000819050us-gaap:FairValueInputsLevel1Memberus-gaap:FairValueMeasurementsRecurringMember2021-12-310000819050us-gaap:WarrantMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:WarrantMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:WarrantMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:WarrantMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:RestrictedStockUnitsRSUMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:CarnaBiosciencesIncMember2022-02-020000819050bbi:VoronoiIncMember2021-08-272021-08-2700008190502021-08-272021-08-270000819050bbi:KakenMemberbbi:MilestonePaymentsMembersrt:MaximumMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:KakenMembersrt:MaximumMemberus-gaap:RoyaltyMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMemberus-gaap:RoyaltyMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberus-gaap:RoyaltyMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:CollaborativeArrangementMemberus-gaap:RoyaltyMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberus-gaap:RoyaltyMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:MilestonePaymentsMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:PaymentCriteriaOneMemberbbi:BotanixMemberbbi:MilestonePaymentsMembersrt:MaximumMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:PaymentCriteriaTwoMemberbbi:MilestonePaymentsMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:PaymentCriteriaThreeMember2022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:UpfrontFeeMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:ReimbursableDevelopmentExpendituresMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:ConsultingServicesMemberbbi:BotanixMemberus-gaap:CollaborativeArrangementMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:ConsultingServicesMemberbbi:BotanixMemberus-gaap:CollaborativeArrangementMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:SublicenseIncomeMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMemberbbi:SublicenseIncomeMemberus-gaap:PrepaidExpensesAndOtherCurrentAssetsMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:ConsultingServicesMemberbbi:BotanixMember2022-05-032022-05-030000819050bbi:BotanixMember2022-05-032022-05-030000819050bbi:BodorLaboratoriesInc.Member2022-05-032022-05-030000819050bbi:BodorLaboratoriesInc.Member2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BodorLaboratoriesInc.Member2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050bbi:BotanixMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:PaycheckProtectionProgramMember2020-04-15bbi:renewalTerm0000819050us-gaap:WarrantMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:SharebasedPaymentArrangementOptionOutstandingMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:A2020OmnibusPlanMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-06-300000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:October2021OfferingMember2021-10-012021-10-310000819050bbi:October2021OfferingMember2021-10-310000819050bbi:July2021PublicOfferingMember2021-07-012021-07-310000819050bbi:July2021PublicOfferingMember2021-07-310000819050us-gaap:CommonStockMemberbbi:October2020OfferingMember2020-10-012020-10-310000819050bbi:October2020OfferingMemberbbi:CommonStockWarrantsMember2020-10-310000819050bbi:October2020OfferingMember2020-10-310000819050bbi:PreFundedWarrantMemberbbi:October2020OfferingMember2020-10-310000819050bbi:CommonStockWarrantsMember2021-06-3000008190502020-10-012020-10-310000819050bbi:PreFundedWarrantMember2020-10-310000819050bbi:October2020OfferingMember2020-10-012020-10-310000819050bbi:October2020OfferingMember2021-06-300000819050bbi:October2020OfferingMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMember2020-06-300000819050bbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMemberbbi:PreFundedWarrantMember2020-06-300000819050bbi:AccompanyingCommonWarrantMemberbbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMember2020-06-300000819050bbi:PreFundedWarrantMember2020-06-300000819050bbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMember2020-06-012020-06-3000008190502020-06-012020-06-300000819050bbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMember2021-06-300000819050bbi:CommonStockPublicOfferingMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-03-310000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050bbi:A2021AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2020-04-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMember2021-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementScenario2Member2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementScenario2Member2021-06-300000819050bbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementScenario2Member2022-06-300000819050bbi:PrivatePlacementOfferingsMember2020-02-290000819050us-gaap:SeriesAMemberbbi:PrivatePlacementOfferingsMember2020-02-290000819050us-gaap:SeriesBMemberbbi:PrivatePlacementOfferingsMember2020-02-290000819050bbi:PrivatePlacementOfferingsMember2020-02-012020-02-290000819050bbi:LincolnParkMember2020-02-290000819050bbi:LincolnParkMember2020-02-012020-02-290000819050bbi:LincolnParkMemberbbi:PurchaseAgreementMember2020-02-012020-02-290000819050bbi:LincolnParkMemberbbi:PurchaseAgreementMember2020-02-290000819050bbi:RegularPurchaseMemberbbi:LincolnParkMember2020-02-012020-02-290000819050bbi:RegularPurchaseMemberbbi:LincolnParkMember2020-02-290000819050bbi:LincolnParkMemberbbi:PurchaseAgreementMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050bbi:LincolnParkMemberbbi:PurchaseAgreementMember2022-01-012022-06-3000008190502022-05-25bbi:vote0000819050bbi:EquityIncentivePlan2009Memberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:VicalStockIncentivePlanMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-06-300000819050bbi:A2020OmnibusPlanMember2022-05-172022-05-170000819050bbi:A2020OmnibusPlanMemberus-gaap:EmployeeStockOptionMember2022-05-030000819050us-gaap:EmployeeStockMemberbbi:EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050bbi:EmployeeStockPurchasePlanMember2021-04-202022-06-300000819050us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:ResearchAndDevelopmentExpenseMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2022-04-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2021-04-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2022-01-012022-06-300000819050us-gaap:GeneralAndAdministrativeExpenseMember2021-01-012021-06-300000819050us-gaap:SubsequentEventMemberbbi:A2020AtMarketIssuanceSalesAgreementMemberbbi:PreFundedWarrantMember2022-07-012022-08-11
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
(Mark One)
| | | | | |
| ☒ | QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended June 30, 2022
or
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 000-21088
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 93-0948554 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| | | | | | | |
| 5777 Central Avenue, | Boulder, | CO | | | 80301 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) | |
(720) 505-4755
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class | Trading symbol(s) | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common stock, $0.01 par value per share | BBI | The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ |
| | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of August 11, 2022, there were 2,873,965 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding.
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
FORM 10-Q
INDEX
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (“Quarterly Report”) contains forward-looking statements that involve substantial risks and uncertainties for purposes of the safe harbor provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All statements contained in this Quarterly Report other than statements of historical fact, including statements relating to future financial, business, and/or research and clinical performance, conditions, plans, prospects, trends, or strategies and other such matters, including without limitation, our strategy; future operations; future financial position; future liquidity; future revenue and payments of any type; territorial focus; projected expenses; results of operations; the anticipated timing, scope, design, progress, results, and/or reporting of data of ongoing and future nonclinical and clinical trials; intellectual property rights, including the acquisition, validity, term, and enforceability of such; the expected timing and/or results of regulatory submissions and approvals; and prospects for commercializing any product candidates of Brickell or third parties, or research and/or licensing collaborations with, or actions of, its partners, including in the United States (“U.S.”), Japan, South Korea, or any other country, or business development activities with other potential partners. The words “may,” “could,” “should,” “might,” “anticipate,” “reflects,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “will,” evaluate,” “advance,” “excited,” “aim,” “strive,” “help,” “progress,” “select,” “initiate,” “looking forward,” “promise,” “provide,” “commit,” “best-in-class,” “first-in-class,” and similar expressions and their variants, are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Such statements are based on management’s current expectations and involve risks and uncertainties. Actual results and performance could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements as a result of many factors. Unless otherwise mentioned or unless the context requires otherwise, all references in this Quarterly Report to “Brickell,” “Brickell Subsidiary,” “Company,” “we,” “us,” and “our,” or similar references, refer to Brickell Biotech, Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
We based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and trends that we believe may affect our financial condition, results of operations, business strategy and business development activities, pipeline legal status, short-term and long-term business operations and objectives, employees, and financial needs. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties, and assumptions, including those described in Part II, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” in this Quarterly Report, in Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2021, and in Part II, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2022, and under a similar heading in any other periodic or current report we may file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) in the future. Moreover, we operate in a very competitive and rapidly changing environment. New risks emerge quickly and from time to time. It is not possible for our management to predict all risks, nor can we assess the impact of all factors on our business and operations or the extent to which any factor, or combination of factors, may cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in any forward-looking statements we may make. In light of these risks, uncertainties, and assumptions, the future events and trends discussed in this Quarterly Report may not occur and actual results could differ materially and adversely from those anticipated or implied in the forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to revise or publicly release the results of any revision to these forward-looking statements, except as required by law. Given these risks and uncertainties, readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement.
You should read carefully the factors described in Part II, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” in this Quarterly Report to better understand the risks and uncertainties inherent in our business and underlying any forward-looking statements. You are advised to consult any further disclosures we make on related subjects in our future public filings and on our website.
RISK FACTORS SUMMARY
Our business, financial condition, and operating results may be affected by a number of factors, whether currently known or unknown. Any one or more of such factors could directly or indirectly cause our actual results of operations and financial condition to vary materially from past or anticipated future results of operations and financial condition. Any of these factors, in whole or in part, let alone combined with any of the others, could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and stock price. We have provided a summary of some of these risks below, with a more detailed explanation of those and other risks applicable to the Company in Part II, Item 1A. “Risk Factors” in this Quarterly Report.
•Our business depends on the successful continued financing, nonclinical and clinical development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of our pipeline assets.
•Clinical drug development for our pipeline assets is expensive, time-consuming, and uncertain. Any data resulting from our trials may not be favorable for further development.
•Our inability to maintain compliance with continued listing requirements of The Nasdaq Stock Market LLC (“Nasdaq”), including if we are unable to maintain the required minimum closing bid price of our common stock, could result in the delisting of our common stock.
•Major public health issues, and specifically the pandemic and related impacts caused by the ongoing spread of COVID-19 and COVID-19 variants, including in terms of constraints on supply chains and human resource availability, could have an adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations and other aspects of our business and that of our suppliers, contractors, and business partners.
•We have sponsored or supported and in the future expect to sponsor or support clinical trials for our product candidates outside the U.S., and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) and applicable foreign regulatory authorities may not accept data from such trials; in addition, we may not be allowed alone or with local country business partners to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates without first conducting clinical trials in each of these other countries.
•We rely and expect to continue to rely on third-party contractors for supply, manufacture, and distribution of preclinical, clinical, and commercial supplies, and possibly sales and promotion, of any future product candidates.
•We may not be able to obtain, afford, maintain, enforce, or protect our intellectual property rights covering our product candidates, including our autoimmune and inflammatory portfolio, and related technologies, that are of sufficient type, breadth, and term throughout the world.
•If we fail to comply with our obligations under our intellectual property and related license agreements, we could lose license rights that are important to our business. Additionally, these agreements may be subject to disagreement over contract interpretation, which could narrow the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or other key aspects of product development and/or commercialization, or increase our financial or other obligations to our licensors.
•Our receipt of future payments from Botanix SB Inc. (“Botanix”) is contingent on various factors outside of our control, including the successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, by Botanix outside of Japan, the successful continued commercialization of sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (“ECCLOCK®”) by Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (“Kaken”) in Japan, and the sufficiency of funds to pay us and Bodor Laboratories, Inc. (“Bodor”), the licensor of this product.
PART I. FINANCIAL INFORMATION
ITEM 1. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
(unaudited)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| | | |
| June 30,
2022 | | December 31,
2021 |
| | | |
| Assets | | | |
| Current assets: | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 14,480 | | | $ | 26,884 | |
| | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 3,771 | | | 2,716 | |
| Total current assets | 18,251 | | | 29,600 | |
| Property and equipment, net | 45 | | | 58 | |
| Contract asset, net of current portion | 181 | | | — | |
| Operating lease right-of-use asset | 30 | | | 59 | |
| | | |
| Total assets | $ | 18,507 | | | $ | 29,717 | |
Liabilities, redeemable preferred stock, and stockholders’ equity | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 1,263 | | | $ | 1,605 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 1,571 | | | 3,136 | |
| Lease liability, current portion | 36 | | | 69 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Total current liabilities | 2,870 | | | 4,810 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 6) | | | |
| | | |
Redeemable preferred stock, $0.01 par value, 5,000,000 shares authorized as of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021; 1 and 0 shares issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively | — | | — |
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | |
Common stock, $0.01 par value, 300,000,000 shares authorized as of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021; 121,066,161 and 119,377,286 shares issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, respectively | 1,211 | | | 1,194 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 170,350 | | | 169,080 | |
| | | |
| Accumulated deficit | (155,924) | | | (145,367) | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 15,637 | | | 24,907 | |
| Total liabilities, redeemable preferred stock, and stockholders’ equity | $ | 18,507 | | | $ | 29,717 | |
| | | |
See accompanying notes to these condensed consolidated financial statements.
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
(unaudited)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended
June 30, | | Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Revenue | | | | | | | |
| Contract revenue | $ | 4,315 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 4,315 | | | $ | — | |
| Royalty revenue | — | | | 151 | | | 92 | | | 168 | |
| Total revenue | 4,315 | | | 151 | | | 4,407 | | | 168 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Research and development | 1,865 | | | 8,838 | | | 7,878 | | | 14,890 | |
| General and administrative | 3,908 | | | 2,891 | | | 7,394 | | | 5,858 | |
| Total operating expenses | 5,773 | | | 11,729 | | | 15,272 | | | 20,748 | |
| Loss from operations | (1,458) | | | (11,578) | | | (10,865) | | | (20,580) | |
| Other income | 313 | | | 459 | | | 314 | | | 490 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Interest expense | (2) | | | (30) | | | (6) | | | (64) | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders | $ | (1,147) | | | $ | (11,149) | | | $ | (10,557) | | | $ | (20,154) | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | $ | (0.01) | | | $ | (0.16) | | | $ | (0.09) | | | $ | (0.31) | |
| | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average shares used to compute net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders, basic and diluted | 119,486,317 | | | 68,856,370 | | | 119,432,103 | | | 64,646,565 | |
See accompanying notes to these condensed consolidated financial statements.
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF REDEEMABLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands, except share data)
(unaudited)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Series A Redeemable
Preferred Stock | | Common Stock | | Additional
Paid-In-Capital | | | | Accumulated
Deficit | | Total
Stockholders’
Equity |
| Shares | | Par Value | | Shares | | Par Value | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, December 31, 2021 | — | | | $ | — | | | 119,377,286 | | | $ | 1,194 | | | $ | 169,080 | | | | | $ | (145,367) | | | $ | 24,907 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 551 | | | | | — | | | 551 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | | | | (9,410) | | | (9,410) | |
| Balance, March 31, 2022 | — | | — | | | 119,377,286 | | 1,194 | | | 169,631 | | | | | (154,777) | | | 16,048 | |
| Issuance of redeemable preferred stock | 1 | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock issued, net of issuance costs of $46 | — | | — | | | 1,419,970 | | 14 | | | 117 | | | | | — | | | 131 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock for cash under employee stock purchase plan | — | | — | | | 268,905 | | 3 | | | 26 | | | | | — | | | 29 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 576 | | | | | — | | | 576 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | | | | (1,147) | | | (1,147) | |
| Balance, June 30, 2022 | 1 | | $ | — | | | 121,066,161 | | $ | 1,211 | | | $ | 170,350 | | | | | $ | (155,924) | | | $ | 15,637 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | — | | $ | — | | | 53,551,461 | | $ | 536 | | | $ | 132,492 | | | | | $ | (105,893) | | | $ | 27,135 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of warrants | — | | — | | | 12,444,887 | | 124 | | | 8,845 | | | | | — | | | 8,969 | |
Issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs of $50 | — | | — | | | 1,083,548 | | 11 | | | 1,617 | | | | | — | | | 1,628 | |
| Issuance of common stock upon restricted stock unit settlement, net of shares withheld for taxes | — | | — | | | 96,350 | | 1 | | | (53) | | | | | — | | | (52) | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 469 | | | | | — | | | 469 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | | | | (9,005) | | | (9,005) | |
| Balance, March 31, 2021 | — | | | — | | | 67,176,246 | | 672 | | | 143,370 | | | | | (114,898) | | | 29,144 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock issued, net of issuance costs of $259 | — | | — | | | 4,768,976 | | 47 | | | 3,890 | | | | | — | | | 3,937 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | 421 | | | | | — | | | 421 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | | — | | — | | | — | | | | | (11,149) | | | (11,149) | |
| Balance, June 30, 2021 | — | | $ | — | | | 71,945,222 | | $ | 719 | | | $ | 147,681 | | | | | $ | (126,047) | | | $ | 22,353 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying notes to these condensed consolidated financial statements.
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(unaudited, in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| 2022 | | 2021 |
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (10,557) | | | $ | (20,154) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | | | |
| Stock-based compensation | 1,127 | | | 890 | |
| Depreciation | 13 | | | 8 | |
| | | |
| Gain on loan extinguishment | — | | | (437) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets, including long-term portion of contract asset | (1,240) | | | (1,092) | |
| Accounts payable | (342) | | | 1,932 | |
| Accrued liabilities | (1,510) | | | (1,352) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | (12,509) | | | (20,205) | |
| | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | | | |
| Capital expenditures | — | | | (36) | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | — | | | (36) | |
| | | |
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Proceeds from the issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs | 131 | | | 5,565 | |
| Payments of taxes related to net share settlement of equity awards | (55) | | | — | |
| Proceeds from the issuance of commons stock under employee stock purchase program | 29 | | | — | |
| Proceeds from the exercise of warrants | — | | | 8,969 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 105 | | | 14,534 | |
| | | |
| NET DECREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | (12,404) | | | (5,707) | |
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—BEGINNING | 26,884 | | | 30,115 | |
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—ENDING | $ | 14,480 | | | $ | 24,408 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Supplemental Disclosure of Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities: | | | |
| Forgiveness of Paycheck Protection Program loan | $ | — | | | $ | 437 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
See accompanying notes to these condensed consolidated financial statements.
BRICKELL BIOTECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(unaudited)
NOTE 1. ORGANIZATION AND NATURE OF OPERATIONS
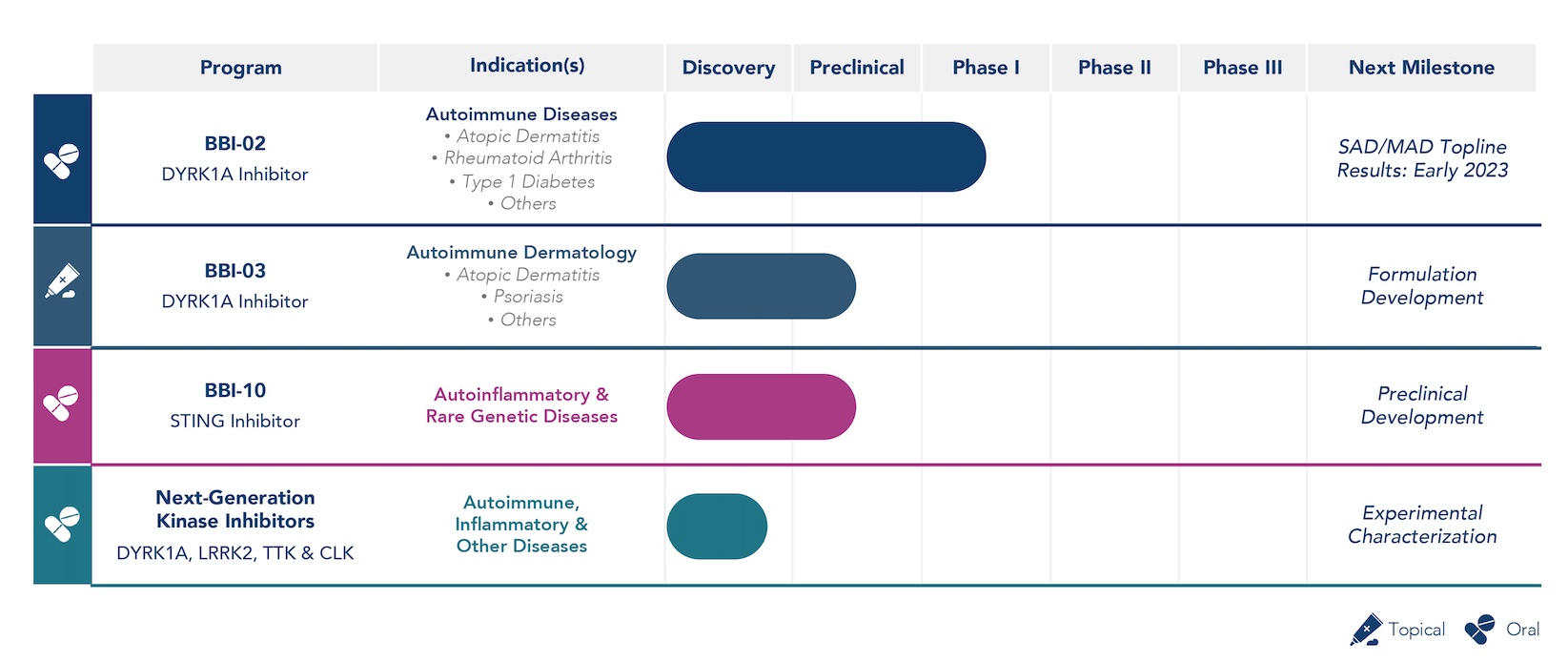
Brickell Biotech, Inc. (the “Company” or “Brickell”) is a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company striving to transform patient lives by developing innovative and differentiated prescription therapeutics for the treatment of autoimmune, inflammatory, and other debilitating diseases. Brickell’s pipeline consists of several development-stage candidates and a cutting-edge platform with broad potential in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. This includes: BBI-02, a novel, clinical-stage, potential first-in-class, oral DYRK1A inhibitor with strong preclinical validation for treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and type 1 diabetes; BBI-10, a novel, preclinical-stage oral Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) inhibitor that has demonstrated dose-dependent cytokine reduction in nonclinical studies providing proof of mechanism for the potential treatment of autoinflammatory and rare genetic diseases; and a platform of next-generation DYRK, CDC2-like kinase (CLK), Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (LRRK2), and TTK protein kinase (TTK), also known as Monopolar spindle 1 (Mps1) kinase, inhibitors with the potential to produce treatments for autoimmune, inflammatory, and other debilitating conditions. Brickell’s executive management team and board of directors bring extensive experience in product development and global commercialization, having served in senior leadership roles at large global pharmaceutical companies and biotechs that have developed and/or launched successful products, including several that were first-in-class and/or achieved iconic status, such as Cialis®, Taltz®, Gemzar®, Prozac®, Cymbalta®, Juvederm®, Pluvicto®, and Sofpironium Bromide. Brickell’s strategy is to leverage this experience to in-license, acquire, develop, and commercialize innovative pharmaceutical products that Brickell believes can meaningfully benefit patients who are suffering from chronic, debilitating diseases that are underserved by available therapies.
Reverse Stock Split
Effective July 5, 2022, the Company effected a 1-for-45 reverse stock split of outstanding shares of its common stock. Share and per share amounts reported as of and prior to June 30, 2022 in the condensed consolidated financial statements and notes do not reflect the adjusted share and per share amounts that were effective on and after July 5, 2022, unless otherwise noted. Additional details of the reverse stock split are reported in Note 7. “Capital Stock.”
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company has incurred significant operating losses and has an accumulated deficit as a result of ongoing efforts to in-license and develop product candidates, including conducting preclinical and clinical trials and providing general and administrative support for these operations. For the six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company had a net loss of $10.6 million and net cash used in operating activities of $12.5 million. As of June 30, 2022, the Company had cash and cash equivalents of $14.5 million and an accumulated deficit of $155.9 million.
The Company believes that its cash and cash equivalents as of June 30, 2022, combined with $2.0 million from expected near-term payments from Botanix SB Inc. (“Botanix”) under the Asset Purchase Agreement (as defined in Note 3. “Strategic Agreements”), will be sufficient to fund its operations for at least the next 12 months. The Company expects to continue to incur additional substantial losses in the foreseeable future as a result of the Company’s research and development activities. Additional funding will be required in the future to continue with the Company’s planned development and other activities. However, the Company may be unable to raise additional funds, which would have a negative impact on the Company’s business, financial condition, and the Company’s ability to develop its pipeline. To the extent that additional funds are raised through the sale of equity, the issuance of securities will result in dilution to the Company’s stockholders.
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Brickell Subsidiary, Inc. (“Brickell Subsidiary”), and are presented in United States (“U.S.”) dollars and have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”) and applicable rules and regulations of the SEC for interim reporting. As permitted under those rules and regulations, certain footnotes or other financial information normally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP have been condensed or omitted. These condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the same basis as the annual financial statements and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, which are necessary for a fair presentation of the Company’s financial information. The results of operations for the three and six months ended June 30, 2022 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the full year ending December 31, 2022, for any other interim period, or for any other future period. The condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2021 has been derived from audited financial statements at that date but does not include all of the information required by U.S. GAAP for complete financial statements. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The Company operates in one operating segment and, accordingly, no segment disclosures have been presented herein.
Use of Estimates
The Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP, which requires it to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Although these estimates are based on the Company’s knowledge of current events and actions it may take in the future, actual results may ultimately differ from these estimates and assumptions.
Risks and Uncertainties
The Company’s business is subject to significant risks common to early-stage companies in the pharmaceutical industry including, but not limited to, the ability to develop appropriate formulations, scale up and produce the compounds; dependence on collaborative parties; uncertainties associated with obtaining and enforcing patents and other intellectual property rights; clinical implementation and success; the lengthy and expensive regulatory approval process; compliance with regulatory and other legal requirements; competition from other products; uncertainty of broad adoption of its approved products, if any, by physicians and patients; significant competition; ability to manage third-party manufacturers, suppliers, contract research organizations, business partners and other alliances; and obtaining additional financing to fund the Company’s efforts.
The Company expects to incur substantial operating losses for the next several years and will need to obtain additional financing in order to develop its product candidates. There can be no assurance that such financing will be available or will be at terms acceptable to the Company.
Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is the price that the Company would receive to sell an asset or pay to transfer a liability in a timely transaction with an independent counterparty in the principal market, or in the absence of a principal market, the most advantageous market for the asset or liability. A three-tier hierarchy distinguishes between (1) inputs that reflect the assumptions market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability developed based on market
data obtained from sources independent of the reporting entity (observable inputs) and (2) inputs that reflect the reporting entity’s own assumptions about the assumptions market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability developed based on the best information available in the circumstances (unobservable inputs). The hierarchy is summarized in the three broad levels listed below:
Level 1—quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities
Level 2—other significant observable inputs (including quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities, interest rates, credit risk, etc.)
Level 3—significant unobservable inputs (including the Company’s own assumptions in determining the fair value of assets and liabilities)
The following table sets forth the fair value of the Company’s financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis based on the three-tier fair value hierarchy (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Level 1 | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| June 30,
2022 | | December 31,
2021 | |
Assets: | | | | | | | |
| Money market funds | $ | 13,480 | | | $ | 25,875 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The following methods and assumptions were used by the Company in estimating the fair values of each class of financial instrument disclosed herein:
Money Market Funds—The carrying amounts reported as cash and cash equivalents in the condensed consolidated balance sheets approximate their fair values due to their short-term nature and/or market rates of interest (Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy).
The carrying values of cash equivalents, other current assets, accounts payable, and accrued liabilities approximate fair value due to the short-term maturity of those items.
Revenue Recognition
The Company has recognized revenue primarily from royalty fees received under the Kaken Agreement and upfront fees, research reimbursements, and sublicense income received under the Asset Purchase Agreement described in Note 3. “Strategic Agreements.” The terms of the agreements may include non-refundable upfront fees, funding of research and development activities, payments based upon achievement of milestones, and various sales-based payments.
The Company recognizes revenue upon the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In determining the appropriate amount of revenue to be recognized, the Company performs the following five steps: (i) identify the contract(s) with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligations in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price, including the constraint on variable consideration; (iv) allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations in the contract; and (v) recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the performance obligations. At contract inception, the Company assesses the goods or services promised within each contract and assesses whether each promised good or service is distinct and determines those that are performance obligations. The Company then recognizes as revenue the amount of the
transaction price that is allocated to the respective performance obligation when (or as) the performance obligation is satisfied.
The Company utilizes judgment to assess the nature of the performance obligation to determine whether the performance obligation is satisfied over time or at a point in time and, if over time, the appropriate method of measuring progress. The Company evaluates the measure of progress each reporting period and, if necessary, adjusts the measure of performance and related revenue recognition.
Contract Revenue
The Company evaluates its contracts, including asset sale arrangements that involve the Company’s rights to intellectual property, to determine whether they are outputs of the Company’s ordinary activities and whether the counterparty meets the definition of a customer. If the arrangement is determined to be a contract with a customer and the goods or services sold are determined to be distinct from other performance obligations identified in the arrangement, the Company recognizes revenue primarily from non-refundable upfront fees, milestone payments, and sales-based payments allocated to the goods or services when (or as) control is transferred to the customer, and the customer can use and benefit from the goods or services.
Licenses of Intellectual Property
If a license for the Company’s intellectual property is determined to be distinct from the other performance obligations identified in the arrangement, the Company recognizes revenue when the license is transferred to the customer, and the customer can use and benefit from the license.
Milestones
At the inception of each arrangement that includes milestone payments (variable consideration), excluding sales-based milestone payments discussed below, the Company evaluates whether the milestones are considered probable of being reached and estimates the amount to be included in the transaction price using the most likely amount method. The most likely amount method is generally utilized when there are only two possible outcomes and represents the Company’s best estimate of the single most likely outcome to be achieved. If it is probable that a significant revenue reversal would not occur, the variable consideration for the associated milestone is included in the transaction price. Milestone payments contingent on regulatory approvals that are not within the Company and the Company’s collaboration partner’s control, as applicable, are generally not considered probable of being achieved until those approvals are received. At the end of each subsequent reporting period, the Company re-evaluates the probability of achievement of milestones and any related constraint, and if necessary, adjusts the Company’s estimate of the variable consideration. Any such adjustments are recorded on a cumulative catch-up basis, which would affect revenue in the period of adjustment.
Sales-Based Payments
For license arrangements that include sales-based payments such as royalties or milestone payments based on the level of sales, and for which the license is deemed to be the predominant item to which the sales-based payments relate, the Company recognizes revenue at the later of (i) when the related sales occur or (ii) when the performance obligation to which some or all of the sales-based payment has been allocated has been satisfied (or partially satisfied). Sales-based payments received under license arrangements are recorded as royalty revenue in the Company’s condensed consolidated statements of operations.
For non-license arrangements that include sales-based payments, including earnout payments and milestone payments based on the level of sales, the Company estimates the sales-based payments (variable consideration) to be achieved and recognizes revenue to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal in the amount of
cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. The Company may use either the most likely amount, as described above, or the expected value method, in making such estimates based on the nature of the payment to be received and whether there is a wide range of outcomes or only two possible outcomes. The expected value method represents the sum of probability-weighted amounts in a range of possible consideration amounts. The Company bases its estimates using the applicable method described above on factors such as, but not limited to, required regulatory approvals, historical sales levels, market events and projections, and other factors as appropriate. The Company updates its estimates at each reporting period based on actual results and future expectations as necessary.
Contract Asset
For non-license arrangements involving the upfront sale and transfer of the Company’s intellectual property rights, the Company recognizes estimated variable consideration as revenue as discussed above before the customer pays consideration or before payment is due. The excess revenue recognized is presented as a contract asset on the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheets. Actual amounts paid or due by the customer are recorded as a reduction to the contract asset. Any revisions to the Company’s estimated revenue based on actual results and future expectations are recognized as an adjustment to the contract asset.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are charged to expense when incurred and consist of costs incurred for independent and collaboration research and development activities. The major components of research and development costs include formulation development, nonclinical studies, clinical studies, clinical manufacturing costs, in-licensing fees for development-stage assets, salaries and employee benefits, and allocations of various overhead and occupancy costs. Research costs typically consist of applied research, preclinical, and toxicology work. Pharmaceutical manufacturing development costs consist of product formulation, chemical analysis, and the transfer and scale-up of manufacturing at contract manufacturers. Assets acquired (or in-licensed) that are utilized in research and development that have no alternative future use are expensed as incurred. Milestone payments related to the Company’s acquired (or in-licensed) assets are recorded as research and development expenses when probable and reasonably estimable.
The Company has entered into and may continue to enter into licensing or subscription arrangements to access and utilize certain technology. In each case, the Company evaluates if the license agreement results in the acquisition of an asset or a business. To date, none of the Company’s license agreements have been considered an acquisition of a business. For asset acquisitions, the upfront payments to acquire such licenses, as well as any future milestone payments made before product approval that do not meet the definition of a derivative, are immediately recognized as research and development expenses when they are paid or become payable, provided there is no alternative future use of the rights in other research and development projects.
Clinical Trial Accruals
Expense accruals related to clinical trials are based on the Company’s estimates of services received and efforts expended pursuant to contracts with multiple research institutions and third-party clinical research organizations that conduct and manage clinical trials on the Company’s behalf. The financial terms of these agreements vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Payments under some of these contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment of patients and the completion of clinical trial milestones. In accruing costs, the Company estimates the period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period based upon patient enrollment, clinical site activations, or information provided to the Company by its vendors on their actual costs incurred. Any estimates of the level of services performed or the costs of these services could differ from actual results.
Net Loss per Share
Basic and diluted net loss per share is computed by dividing net loss by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. When the effects are not anti-dilutive, diluted earnings per share is computed by dividing the Company’s net income by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding and the impact of all potentially dilutive common shares. Diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share, as the effects of potentially dilutive securities are anti-dilutive for all periods presented.
The following table sets forth the potential common shares excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Three and Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| | | | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Outstanding warrants | | | | | 27,944,544 | | | 27,944,544 | |
| Outstanding options | | | | | 10,449,516 | | | 6,716,167 | |
| Unvested restricted stock units | | | | | — | | | 47,435 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | | | | | 38,394,060 | | | 34,708,146 | |
Leases
The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at inception. Operating leases with a term greater than one year are recognized on the balance sheet as right-of-use assets, lease liabilities and, if applicable, long-term lease liabilities. The Company does not currently hold any financing leases. The Company has elected the practical expedient not to recognize on the balance sheet leases with terms of one year or less and not to separate lease components and non-lease components for long-term real estate leases. Lease liabilities and their corresponding right-of-use assets are recorded based on the present value of lease payments over the expected lease term. The interest rate implicit in lease contracts is typically not readily determinable. As such, the Company estimates the incremental borrowing rate in determining the present value of lease payments. The Company’s headquarters operating lease has one single component. The lease component results in a right-of-use asset being recorded on the balance sheet, which is amortized as lease expense on a straight-line basis in the Company’s condensed consolidated statements of operations.
Redeemable Preferred Stock
The Company issued one share of redeemable preferred stock in May 2022. The redeemable preferred stock contained provisions that required redemption under circumstances that were outside of the Company’s control and was classified as a mezzanine instrument outside of the Company’s capital accounts. The share of redeemable preferred stock was sold to one investor for $10 and was subsequently redeemed in July 2022, as described further in Note 7. “Capital Stock.”
New Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board or other standard setting bodies that the Company adopts as of the specified effective date. The Company does not believe that the adoption of recently issued standards has had or will have a material impact on the Company's condensed consolidated financial statements or disclosures.
NOTE 3. STRATEGIC AGREEMENTS
Exclusive License and Development Agreement with Carna
On February 2, 2022, the Company entered into an Exclusive License Agreement (the “Carna License Agreement”) with Carna Biosciences, Inc. (“Carna”), pursuant to which the Company acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize Carna’s portfolio of novel STING inhibitors. In accordance with the terms of the Carna License Agreement, in exchange for the licensed rights, the Company made a one-time cash payment of $2.0 million, which was recorded as research and development expenses in the condensed consolidated statements of operations during the six months ended June 30, 2022.
The Carna License Agreement provides that the Company will make success-based payments to Carna of up to $258.0 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. Further, the Carna License Agreement provides that the Company will pay Carna tiered royalty payments ranging from mid-single digits up to 10% of net sales. All of the contingent payments and royalties are payable in cash in U.S. Dollars. Under the terms of the Carna License Agreement, the Company is responsible for, and bears the future costs of, all development and commercialization activities, including patenting, related to all the licensed compounds. As of June 30, 2022 and through the date of this Quarterly Report, the Company has not yet made any payments or recorded any liabilities related to the specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones or royalties on net sales pursuant to the Carna License Agreement.
License and Development Agreement with Voronoi
On August 27, 2021, the Company entered into a License and Development Agreement (the “Voronoi License Agreement”) with Voronoi Inc. (“Voronoi”), pursuant to which the Company acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize BBI-02, a novel, clinical-stage, potential first-in-class, oral DYRK1A inhibitor, and other next-generation kinase inhibitors. In accordance with the terms of the Voronoi License Agreement, in exchange for the licensed rights, the Company made a one-time payment of $2.5 million in cash and issued $2.0 million, or 2,816,901 shares, of its common stock to Voronoi.
With respect to BBI-02, the Voronoi License Agreement provides that the Company will make payments to Voronoi of up to $211.0 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. With respect to the next-generation compounds arising from the novel kinase inhibitor platform, the Company will make payments to Voronoi of up to $107.5 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. Further, the Voronoi License Agreement provides that the Company will pay Voronoi tiered royalty payments ranging from low-single digits up to 10% of net sales of products arising from the DYRK1A inhibitor programs and next-generation kinase inhibitor platform. All of the contingent payments and royalties are payable in cash in U.S. Dollars, except for $1.0 million of the development and regulatory milestone payments, which amount is payable in equivalent shares of the Company’s common stock. Under the terms of the Voronoi License Agreement, the Company is responsible for, and bears the future costs of, all development and commercialization activities, including patenting, related to all the licensed compounds. As of June 30, 2022 and through the date of this Quarterly Report, the Company has not yet made any payments or recorded any liabilities related to the specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones or royalties on net sales pursuant to the Voronoi License Agreement.
Asset Purchase Agreement with Botanix
On May 3, 2022 (the “Effective Date”), the Company and Brickell Subsidiary entered into an asset purchase agreement with Botanix and Botanix Pharmaceuticals Limited (the “Asset Purchase Agreement”), pursuant to which Botanix acquired and assumed control of all rights, title, and interests to assets primarily related to the
proprietary compound sofpironium bromide that were owned and/or licensed by the Company or Brickell Subsidiary (the “Assets”). The Company had previously entered into a License Agreement with Bodor Laboratories, Inc. (“Bodor”), dated December 15, 2012 (last amended in February 2020) that provided the Company with a worldwide exclusive license to develop, manufacture, market, sell, and sublicense products containing sofpironium bromide through which the Assets were developed (the “Amended and Restated License Agreement”). As a result of the Asset Purchase Agreement, Botanix is now responsible for all further research, development, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide globally and replaced the Company as the exclusive licensee under the Amended and Restated License Agreement.
In accordance with the sublicense rights provided to the Company under the Amended and Restated License Agreement, the Company also previously entered into a License, Development, and Commercialization Agreement with Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (“Kaken”), dated as of March 31, 2015 (as amended in May 2018, the “Kaken Agreement”), under which the Company granted to Kaken an exclusive right to develop, manufacture, and commercialize the sofpironium bromide compound in Japan and certain other Asian countries (the “Territory”). In exchange for the sublicense, the Company was entitled to receive aggregate payments of up to $10.0 million upon the achievement of specified development milestones, which was earned and received in 2017 and 2018, and up to $19.0 million upon the achievement of sales-based milestones, as well as tiered royalties based on a percentage of net sales of licensed products in the Territory. In September 2020, Kaken received regulatory approval in Japan to manufacture and market sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (ECCLOCK®) for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis, and as a result, the Company began recognizing royalty revenue earned on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK in Japan. Pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Kaken Agreement was also assigned to Botanix, which replaced the Company as the exclusive sub-licensor to Kaken. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, prior to entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Company recognized royalty revenue of $0 and $0.2 million, respectively, under the Kaken Agreement. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, the Company recognized royalty revenue of $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
The Company determined that the development of and ultimate sale and assignment of rights to the Assets is an output of the Company’s ordinary activities and Botanix is a customer as it relates to the sale of the Assets and related activities.
In accordance with the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement, in exchange for the Assets, the Company (i) received an upfront payment at closing in the amount of $3.0 million, (ii) is to be reimbursed for certain recent development expenditures in advancement of the Assets, and (iii) will receive from Botanix contingent near-term milestone payments of (a) $2.0 million upon the acceptance by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) of the filing of a new drug application (“NDA”) for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, and (b) $4.0 million if marketing approval in the U.S. for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, is received on or before September 30, 2023, or $2.5 million if such marketing approval is received after September 30, 2023 but on or before February 17, 2024. The Company also is eligible to receive additional success-based regulatory and sales milestone payments of up to $168 million. Further, the Company will receive tiered earnout payments ranging from high-single digits to mid-teen digits on net sales of sofpironium bromide gel (the “Earnout Payments”).
The Asset Purchase Agreement also provides that Botanix will pay to the Company a portion of the sales-based milestone payments and royalties that Botanix receives from Kaken under the Kaken Agreement (together, the “Sublicense Income”). During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company recorded contract revenue for the upfront payment received by the Company from Botanix of $3.0 million, reimbursed development expenditures from Botanix under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.6 million, and fees for consulting services the Company provided under the TSA (as defined below) of $0.4 million. Additionally, during the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company recognized contract revenue of $0.3 million related to the Sublicense Income, which represents the Company’s estimate of payments that will be earned by the Company in the applicable period from royalties Botanix will receive from Kaken to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. Such payments vary
based on net sales that are impacted by a wide variety of market and other factors and, as such, the Company utilized the expected value approach, which the Company believes will best predict the amount of consideration to which it will be entitled. In relation to the sales-based milestone payments that Botanix may receive from Kaken in the future, the Company utilized the most likely amount method and determined it is not yet probable that the Company will receive any payments from Botanix in relation to such milestone payments. Therefore, the Company determined that such milestone payments are fully constrained as of June 30, 2022, and, as such, have not yet been recognized as contract revenue.
All other consideration due under the Asset Purchase Agreement is contingent upon certain regulatory approvals and future sales subsequent to such regulatory approvals or is based upon future sales that the Company determined are not yet probable due to such revenues being highly susceptible to factors outside of the Company’s influence and uncertainty about the amount of such consideration that will not be resolved for an extended period of time. Therefore, the Company determined that such variable consideration amounts are fully constrained as of June 30, 2022, and as such, did not recognize such amounts as contract revenue.
With respect to the recognition of contract revenue for the Sublicense Income based on future royalties that will be due to Botanix from Kaken, certain amounts are not yet due from Botanix. Therefore, the Company has recorded a contract asset equal to the amount of revenue recognized to date related to the Sublicense Income, less the amount of payments received from or due by Botanix in relation to the Sublicense Income to date. As of June 30, 2022, the contract asset related to the Sublicense Income is $0.3 million, of which $0.2 million is included within prepaid expenses and other current assets in the condensed consolidated balance sheet.
Transition Services Agreement with Botanix
In connection with the sale of the Assets, on the Effective Date, the Company and Botanix entered into a transition services agreement (the “TSA”) whereby the Company is providing consulting services as an independent contractor to Botanix in support of and through filing and potential approval of the U.S. NDA for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%. In accordance with the terms of the TSA, in exchange for providing these services, the Company will receive from Botanix, (i) prior to the acceptance of the filing by the FDA of such NDA, a fixed monthly amount of $71 thousand, and (ii) after the acceptance of the filing by the FDA of such NDA, a variable amount based upon actual hours worked, in each case plus related fees and expenses of the Company’s advisors (plus a 5% administrative fee) and the Company’s out-of-pocket expenses. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company recognized contract revenue of $0.4 million related to these services.
Agreements with Bodor
In connection with the sale of the Assets, on the Effective Date, the Company, Brickell Subsidiary, and Bodor entered into an agreement (the “Rights Agreement”) to clarify that the Company and Brickell Subsidiary have the power and authority under the Amended and Restated License Agreement to enter into the Asset Purchase Agreement and the TSA, and that Botanix would assume the Amended and Restated License Agreement pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement. The Rights Agreement includes a general release of claims and no admission of liability between the parties. Pursuant to such Rights Agreement, the Company has agreed to pay Bodor (i) 18% of the amount of each payment actually received by the Company from Botanix for upfront and milestone payments under the Asset Purchase Agreement, as well as (ii) certain tiered payments, set as a percentage ranging from mid-single digits to low-teen digits, of the actual amount of each of the applicable Earnout Payments received by the Company from Botanix. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company incurred $0.5 million of general and administrative expenses for payments due to Bodor.
Pursuant to the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Company retained its obligation under the Amended and Restated License Agreement to issue $1.0 million in shares of its common stock to Bodor upon the FDA’s acceptance of an NDA filing for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%. As such regulatory milestone event has not yet
been achieved, no research and development expenses associated with milestones were incurred during the three or six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021. Prior to the execution of the Rights Agreement, the Company paid Bodor immaterial amounts with respect to the royalties the Company received from Kaken for sales of sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (ECCLOCK) in Japan during those periods.
NOTE 4. DETAILED ACCOUNT BALANCES
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| June 30,
2022 | | December 31,
2021 |
| Prepaid clinical trial costs | $ | 2,390 | | | $ | 1,443 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 694 | | | 921 | |
| Accounts receivable | 358 | | | 125 | |
| Other prepaid expenses | 170 | | | 168 | |
| Contract asset | 152 | | | — | |
| Other short-term assets | 7 | | | 59 | |
| Total | $ | 3,771 | | | $ | 2,716 | |
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| | | |
| June 30,
2022 | | December 31,
2021 |
| Accrued compensation | $ | 1,016 | | | $ | 1,861 | |
| Accrued professional fees | 382 | | | 452 | |
| Accrued contracted research and development services | 173 | | | 823 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Total | $ | 1,571 | | | $ | 3,136 | |
NOTE 5. NOTE PAYABLE
On April 15, 2020, the Company executed an unsecured promissory note to IberiaBank (the “PPP Loan”) pursuant to the U.S. Small Business Administration’s Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP”) under Division A, Title I of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (the “CARES Act”). The Company used the PPP Loan proceeds in the principal amount of $0.4 million and bearing interest at a fixed rate of 1.00% per annum to cover payroll costs and certain other permitted costs in accordance with the relevant terms and conditions of the CARES Act. In January 2021, the Company applied for forgiveness of the full amount of the PPP Loan, which was forgiven in full in June 2021. As a result, during the six months ended June 30, 2021, the Company recognized a gain on extinguishment of debt of approximately $0.4 million in the condensed consolidated statements of operations within the line “Other income.”
NOTE 6. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating Lease
In August 2016, the Company entered into a multi-year, noncancelable lease for its Colorado-based office space, which was amended in June 2021 to, among other things, extend the lease term to December 31, 2022 (as amended, the “Boulder Lease”). Under the terms of the Boulder Lease, the Company may, at its option, renew the Boulder Lease for two additional terms of three years each, with monthly rent payments determined at the time of renewal at the lower of $6,076 per month or current market rental rates. The Company recognized a right-of-use asset and corresponding lease liability. Minimum base lease payments under the Boulder Lease are
recognized on a straight-line basis over the full term of the lease. In addition to base rental payments included in the contractual obligations table below, the Company is responsible for its pro rata share of the operating expenses for the building, which includes common area maintenance, utilities, property taxes, and insurance.
Upon modification of the Boulder Lease, the Company reassessed classification of the lease and determined that the lease still met the criteria to be classified as an operating lease. Furthermore, the Company remeasured the lease liability as of the effective date by calculating the present value of the new lease payments, discounted at the Company’s updated incremental borrowing rate of 11.0%, over the extended term of 18 months. The operating expenses are variable and are not included in the present value determination of the lease liability. Because the Company was not reasonably certain to exercise the renewal option, the option was not considered in determining the lease term, and associated potential additional payments were excluded from lease payments.
The following is a summary of the contractual obligations related to operating lease commitments as of June 30, 2022 (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| Total maturities, through December 31, 2022 | | $ | 37 | |
| Less imputed interest | | (1) | |
| Present value of lease liability | | $ | 36 | |
Licensing and Other Agreements
Refer to Note 3. “Strategic Agreements” for more information about the Company’s obligations under its licensing and other agreements.
NOTE 7. CAPITAL STOCK
Common Stock
Under the Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, the Company’s board of directors has the authority to issue up to 300,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.01 per share. Each share of the Company’s common stock is entitled to one vote, and the holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to receive dividends when and as declared or paid by its board of directors. The Company had reserved authorized shares of common stock for future issuance as of June 30, 2022 as follows:
| | | | | |
| June 30,
2022 |
| Common stock warrants | 27,944,544 | |
| Common stock options outstanding | 10,449,516 | |
| Shares available for grant under the Omnibus Plan | 5,627,209 | |
| Shares available for grant under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan | 2,181,810 | |
| |
| |
| |
| Total | 46,203,079 | |
Public Offerings of Common Stock and Warrants
In October 2021, the Company completed a sale of 30,263,400 shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $0.38 per share in an underwritten public offering (the “October 2021 Offering”). The October 2021 Offering resulted in net proceeds of approximately $10.3 million, after deducting the underwriting discount and offering expenses payable by the Company.
In July 2021, the Company completed a sale of 12,983,871 shares of its common stock at a public offering price of $0.62 per share in an underwritten public offering (the “July 2021 Offering”). The July 2021 Offering
resulted in net proceeds of approximately $7.3 million, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company.
In October 2020, the Company completed a sale of 19,003,510 shares of its common stock, and, to certain investors, pre-funded warrants to purchase 1,829,812 shares of its common stock, and accompanying common stock warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 20,833,322 shares of its common stock (the “October 2020 Offering”). Each share of common stock and pre-funded warrant to purchase one share of the Company’s common stock was sold together with a common warrant to purchase one share of the Company’s common stock. The public offering price of each share of the Company’s common stock and accompanying common warrant was $0.72 and $0.719 for each pre-funded warrant and accompanying common warrant, respectively. The shares of common stock and pre-funded warrants, and the accompanying common warrants, were issued separately and were immediately separable upon issuance. The common warrants are exercisable at a price of $0.72 per share of the Company’s common stock and will expire five years from the date of issuance. The pre-funded warrants were exercised in October 2020 at an exercise price of $0.001 per share of the Company’s common stock. The October 2020 Offering resulted in net proceeds of approximately $13.7 million to the Company after deducting underwriting commissions and discounts and other offering expenses payable by the Company of $1.3 million and excluding the proceeds from the exercise of the warrants. During the six months ended June 30, 2021, 12,427,387 common warrants associated with the October 2020 Offering were exercised at a weighted-average exercise price of $0.72 per share, resulting in aggregate proceeds of approximately $8.9 million.
In June 2020, the Company completed a sale of 14,790,133 shares of its common stock, and, to certain investors, pre-funded warrants to purchase 2,709,867 shares of its common stock, and accompanying common stock warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 17,500,000 shares of its common stock (the “June 2020 Offering”). Each share of common stock and pre-funded warrant to purchase one share of common stock was sold together with a common warrant to purchase one share of common stock. The public offering price of each share of common stock and accompanying common warrant was $1.15 and $1.149 for each pre-funded warrant and accompanying common warrant, respectively. The shares of common stock and pre-funded warrants, and the accompanying common warrants, were issued separately and were immediately separable upon issuance. The pre-funded warrants were exercised in the third quarter of 2020 at an exercise price of $0.001 per share of common stock. The common warrants were immediately exercisable at a price of $1.25 per share of common stock and will expire five years from the date of issuance. The June 2020 Offering resulted in approximately $18.7 million of net proceeds to the Company after deducting underwriting commissions and discounts and other offering expenses payable by the Company of $1.4 million and excluding the proceeds from the exercise of the warrants. Certain officers of the Company participated in the June 2020 Offering by purchasing an aggregate purchase price of $0.2 million of the Company's common stock and warrants. During the six months ended June 30, 2021, 17,500 common warrants associated with the June 2020 Offering were exercised at a weighted-average exercise price of $1.25 per share, resulting in aggregate proceeds of approximately $22 thousand.
The Company has used and is using the remaining net proceeds from its common stock offerings for research and development, including clinical trials, working capital, and general corporate purposes.
At Market Issuance Sales Agreements
In March 2021, the Company entered into an At Market Issuance Sales Agreement (the “2021 ATM Agreement”) with Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. (“Oppenheimer”) and William Blair & Company, L.L.C. as the Company’s sales agents (the “Agents”). Pursuant to the terms of the 2021 ATM Agreement, the Company may sell from time to time through the Agents shares of its common stock having an aggregate offering price of up to $50.0 million. Such shares are issued pursuant to the Company’s shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-254037). Sales of the shares are made by means of ordinary brokers’ transactions on The Nasdaq Capital Market at market prices or as otherwise agreed by the Company and the Agents. Under the
terms of the 2021 ATM Agreement, the Company may also sell the shares from time to time to an Agent as principal for its own account at a price to be agreed upon at the time of sale. Any sale of the shares to an Agent as principal would be pursuant to the terms of a separate placement notice between the Company and such Agent. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, the Company sold 1,419,970 shares of common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.12 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $0.2 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to the Agents. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, the Company sold 3,963,476 shares of common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.89 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $3.4 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to the Agents. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $45.9 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold by the Company under the 2021 ATM Agreement.
In April 2020, the Company entered into an At Market Issuance Sales Agreement (the “2020 ATM Agreement” and, together with the 2021 ATM Agreement, the “ATM Agreements”) with Oppenheimer as the Company’s sales agent. Pursuant to the terms of the 2020 ATM Agreement, the Company may sell from time to time through Oppenheimer shares of its common stock having an aggregate offering price of up to $8.0 million. Such shares are issued pursuant to the Company’s shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-236353). Sales of the shares are made by means of ordinary brokers’ transactions on The Nasdaq Capital Market at market prices or as otherwise agreed by the Company and Oppenheimer. Under the terms of the 2020 ATM Agreement, the Company may also sell the shares from time to time to Oppenheimer as principal for its own account at a price to be agreed upon at the time of sale. Any sale of the shares to Oppenheimer as principal would be pursuant to the terms of a separate placement notice between the Company and Oppenheimer. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, no sales of common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement occurred. During the three months ended June 30, 2021, the Company sold 5,500 shares of its common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $1.16 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $6.2 thousand, after giving effect to a 3% commission to Oppenheimer as agent. During the six months ended June 30, 2021, the Company sold 1,089,048 shares of its common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $1.55 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $1.6 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to Oppenheimer as agent. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $2.6 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold by the Company under the 2020 ATM Agreement.
The Company is subject to the SEC’s “baby shelf rules,” which prohibit companies with a public float of less than $75 million from issuing securities under a shelf registration statement in excess of one-third of such company’s public float in a 12-month period. These rules may limit future issuances of shares by the Company under the ATM Agreements or other common stock offerings.
Private Placement Offerings
In February 2020, the Company and Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”) entered into (i) a securities purchase agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”); (ii) a purchase agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”); and (iii) a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”). Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, Lincoln Park purchased, and the Company sold, (i) an aggregate of 950,000 shares of common stock (the “Common Shares”); (ii) a warrant to initially purchase an aggregate of up to 606,420 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.01 per share (the “Series A Warrant”); and (iii) a warrant to initially purchase an aggregate of up to 1,556,420 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $1.16 per share (the “Series B Warrant,” and together with the Series A Warrant, the “Warrants”). The aggregate gross purchase price for the Common Shares and the Warrants was $2.0 million.
Under the terms and subject to the conditions of the Purchase Agreement, the Company has the right, but not the obligation, to sell to Lincoln Park, and Lincoln Park is obligated to purchase, up to $28.0 million in the aggregate of shares of common stock. In order to retain maximum flexibility to issue and sell up to the maximum of $28.0 million of the Company’s common stock under the Purchase Agreement, the Company
sought and, at its annual meeting on April 19, 2021, received, stockholder approval for the sale and issuance of common stock in connection with the Purchase Agreement under Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(d). Sales of common stock by the Company will be subject to certain limitations, and may occur from time to time, at the Company’s sole discretion, over the 36-month period commencing on August 14, 2020 (the “Commencement Date”).
Following the Commencement Date, under the Purchase Agreement, on any business day selected by the Company, the Company may direct Lincoln Park to purchase up to 100,000 shares of common stock on such business day (each, a “Regular Purchase”), provided, however, that (i) the Regular Purchase may be increased to up to 125,000 shares, provided that the closing sale price of the common stock is not below $3.00 on the purchase date; and (ii) the Regular Purchase may be increased to up to 150,000 shares, provided that the closing sale price of the common stock is not below $5.00 on the purchase date. In each case, Lincoln Park’s maximum commitment in any single Regular Purchase may not exceed $1,000,000. The purchase price per share for each such Regular Purchase will be based on prevailing market prices of common stock immediately preceding the time of sale. In addition to Regular Purchases, the Company may direct Lincoln Park to purchase other amounts as accelerated purchases or as additional accelerated purchases if the closing sale price of the common stock exceeds certain threshold prices as set forth in the Purchase Agreement. In all instances, the Company may not sell shares of its common stock to Lincoln Park under the Purchase Agreement if it would result in Lincoln Park beneficially owning more than 9.99% of the outstanding shares of common stock. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, no sales of common stock under the Purchase Agreement occurred. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, the Company sold to Lincoln Park 800,000 shares under the Purchase Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.81 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $0.6 million. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $26.9 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold by the Company under the Purchase Agreement. However, only 57,751 of such shares (less than $175,000 of shares assuming a sale date of August 11, 2022) have been registered by the Company under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
The Company agreed with Lincoln Park that it will not enter into any “variable rate” transactions with any third party, subject to certain exceptions, for a period defined in the Purchase Agreement. The Company has the right to terminate the Purchase Agreement at any time, at no cost or penalty.
The Securities Purchase Agreement, the Purchase Agreement, and the Registration Rights Agreement contain customary representations, warranties, agreements, and conditions to completing future sale transactions, indemnification rights, and obligations of the parties.
Reverse Stock Split
On June 30, 2022, the stockholders of the Company approved an amendment to the Company’s Restated Certificate of Incorporation to effect a reverse stock split of the Company’s outstanding common stock. The Company effected the reverse stock split at a split ratio of 1-for-45 on July 5, 2022, at which date each forty-five (45) shares of common stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the reverse stock split were automatically reclassified, combined, and converted into one (1) validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable share of the Company’s common stock, subject to the treatment of fractional share interests as described below. Proportional adjustments were made to the number of shares of the Company’s common stock subject to outstanding equity awards and warrants, as well as the applicable exercise price.
No fractional shares were issued in connection with the reverse stock split. All fractional shares were aggregated and sold at the then-prevailing prices on The Nasdaq Capital Market on behalf of those stockholders who would otherwise be entitled to receive a fractional share as a result of the reverse stock split. After completion of such sale, stockholders who would have been entitled to a fractional share instead received a cash payment in an amount equal to their respective pro rata shares of the total proceeds of that sale net of any brokerage costs incurred to sell such stock.
Preferred Stock
Under the Company’s amended and restated certificate of incorporation, the Company’s board of directors has the authority to issue up to 5,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.01 per share, at its discretion, in one or more classes or series and to fix the powers, preferences and rights, and the qualifications, limitations, or restrictions thereof, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, and liquidation preferences, without further vote or action by the Company’s stockholders. On May 25, 2022, the Company issued and sold one share of the Company’s preferred stock that was designated as Series A Preferred Stock (the “Series A Preferred Stock”) for a nominal amount. As of June 30, 2022, the outstanding share of Series A Preferred Stock had 80,000,000 votes exclusively with respect to any proposal to amend the Company’s Restated Certificate of Incorporation to effect a reverse stock split of the Company’s common stock. The terms of the Series A Preferred Stock provided that it would be voted, without action by the holder, on any such proposal in the same proportion as shares of the Company’s common stock were voted. The Series A Preferred Stock otherwise had no voting rights except as otherwise required by the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware. The Series A Preferred Stock was not convertible into, or exchangeable for, shares of any other class or series of stock or other securities of the Company and had no rights with respect to any distribution of assets of the Company, including upon a liquidation, bankruptcy, reorganization, merger, acquisition, sale, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntarily or involuntarily. The holder of the Series A Preferred Stock was not entitled to receive dividends of any kind.
The Series A Preferred Stock was redeemed in whole on July 5, 2022 upon the effectiveness of the amendment to the Certificate of Incorporation implementing the reverse stock split. Other than the one share of the Company’s Series A Preferred Stock outstanding as of June 30, 2022, as of such date the Company had not issued or designated the rights, preferences, or privileges of any other class or series of preferred stock.
NOTE 8. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
Equity Incentive Plans
On April 20, 2020, the Company’s stockholders approved the 2020 Omnibus Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “Omnibus Plan”), which replaced, with respect to new award grants, the Company’s 2009 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended and restated (the “2009 Plan”), and the Vical Equity Incentive Plan (the “Vical Plan”) (collectively, the “Prior Plans”) that were previously in effect. Following the approval of the Omnibus Plan on April 20, 2020, no further awards were available to be issued under the Prior Plans, but awards outstanding under those plans as of that date remain outstanding in accordance with their terms. As of June 30, 2022, 1,224,091 and 111,373 shares were subject to outstanding awards under the 2009 Plan and Vical Plan, respectively.
On May 17, 2022, the Company’s stockholders approved an increase in the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the Omnibus Plan by 5,372,000 shares. As of June 30, 2022, 14,551,389 shares were authorized and 9,114,082 shares were subject to outstanding awards under the Omnibus Plan. As of June 30, 2022, 5,627,209 shares remained available for grant under the Omnibus Plan.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
On April 19, 2021, the Company’s stockholders approved the Brickell Biotech, Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”), which had a first eligible purchase period commencing on July 1, 2021. The ESPP allows qualified employees to purchase shares of the Company’s common stock at a price per share equal to 85% of the lower of: (i) the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the first trading day of the applicable purchase period or (ii) the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the last trading day of the applicable purchase period. New six-month purchase periods begin each January 1 and July 1. As of June 30,
2022, the Company had 2,181,810 shares available for issuance and 418,190 cumulative shares had been issued under the ESPP.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
Total stock-based compensation expense reported in the condensed consolidated statements of operations was allocated as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended
June 30, | | Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| Research and development | $ | 113 | | | $ | 88 | | | $ | 216 | | | $ | 197 | |
| General and administrative | 463 | | | 333 | | | 911 | | | 693 | |
| Total stock-based compensation expense | $ | 576 | | | $ | 421 | | | $ | 1,127 | | | $ | 890 | |
NOTE 9. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
At Market Issuance Sales Agreements
Subsequent to June 30, 2022 and through August 11, 2022, the Company sold shares of common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $0.7 million.
Nasdaq Minimum Bid Price Compliance
On July 19, 2022, the Company received formal notice from The Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”) stating that it regained compliance with the minimum bid price requirement for continued listing on Nasdaq and, accordingly, that the previously-scheduled hearing regarding the delisting action had been canceled and the Company’s common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq.
ITEM 2. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
We are a clinical-stage pharmaceutical company striving to transform patient lives by developing innovative and differentiated prescription therapeutics for the treatment of autoimmune, inflammatory, and other debilitating diseases. Our pipeline consists of several development-stage candidates and a cutting-edge platform with broad potential in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders. Our executive management team and board of directors bring extensive experience in product development and global commercialization, having served in senior leadership roles at large global pharmaceutical companies and biotechs that have developed and/or launched successful products, including several that were first-in-class and/or achieved iconic status, such as Cialis®, Taltz®, Gemzar®, Prozac®, Cymbalta®, Juvederm®, Pluvicto®, and Sofpironium Bromide. Our strategy is to leverage this experience to in-license, acquire, develop, and commercialize innovative pharmaceutical products that we believe can meaningfully benefit patients who are suffering from chronic, debilitating diseases that are underserved by available therapies. We have demonstrated our success with this strategy by developing sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, a novel treatment for primary axillary hyperhidrosis, from an early preclinical stage through a successful Phase 3 program in the U.S. and through marketing approval and commercial launch in Japan with our former partner Kaken, culminating in the sale of our rights in sofpironium bromide to Botanix.
The following image summarizes our current pipeline and corresponding development programs:
Research & Development Programs
BBI-02: A Potential First-in-Class Oral DYRK1A Inhibitor for the Treatment of Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
In August 2021, we entered into a License and Development Agreement (the “Voronoi License Agreement”) with Voronoi Inc. (“Voronoi”), pursuant to which we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize BBI-02, a novel, clinical-stage, potential first-in-class, highly selective, and orally bioavailable small molecule DYRK1A inhibitor that aims to restore immune balance in patients whose immune systems have become dysregulated. Based on the promising preclinical efficacy data generated to date, we believe BBI-02 has the potential to be a first-in-class, potent therapy for the treatment of a wide array of debilitating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
BBI-02 is our lead development-stage program and has demonstrated promising results in various preclinical models, including for atopic dermatitis (“AD”) and rheumatoid arthritis. In these models, BBI-02 showed encouraging decreases in disease severity and reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines compared to current standard-of-care agents, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors and anti-tumor necrosis factor (“TNF”) biologics. Notably, many current therapies for autoimmune disorders are broadly immunosuppressive, which may lead to severe side effects, such as increased infection risk. Preclinical data have shown BBI-02 to drive regulatory T-cell differentiation while dampening pro-inflammatory TH17 cells and MyD88/IRAK4-related signaling pathways. Regulatory T-cells serve to maintain tolerance and keep the autoreactive, pro-inflammatory T-cells in check, thus inhibiting autoimmune disease and limiting chronic inflammation. The myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (“MyD88”) protein is normally spliced into a long form and a short form. DYRK1A inhibition shifts the balance to produce more MyD88 short form, which leads to IRAK4, a protein kinase involved in signaling immune responses from toll-like receptors, not being phosphorylated and so appears to deactivate downstream cascades of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines. Based on current understanding, this inhibition of the release of excess cytokines can be achieved by re-establishing the role of MyD88 short form as a negative regulator of this pathway. Unlike many existing therapies, as well as those currently being investigated, BBI-02 may have the ability to target both the adaptive and innate immune imbalance simultaneously, potentially resulting in, or substantially achieving, restoration of immune homeostasis that, if proven, would represent a paradigm shift in the treatment of certain autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.
In May 2022, we initiated a first-in-human Phase 1 clinical trial for BBI-02 (“BBI-02-101”) in Canada, which marks the first time a DYRK1A inhibitor intended for patients with autoimmune diseases has been administered
in humans. BBI-02-101 is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of BBI-02 capsules in both healthy subjects and patients with AD. In the first quarter of 2022, we successfully submitted a Clinical Trial Application for BBI-02 to Health Canada and subsequently received a No Objection Letter, allowing the BBI-02-101 study to proceed as planned. Part 1A of the study is a single ascending dose (“SAD”) assessment of BBI-02 capsules or placebo in up to 56 healthy subjects across seven cohorts at one study center. Part 1B of the study will be a multiple ascending dose (“MAD”) assessment of BBI-02 capsules or placebo administered once daily for 14 days. The MAD part of the study is expected to enroll a total of 33 healthy subjects across three cohorts at one study center. Part 2 of the study will compare BBI-02 to placebo in AD patients over 28 days of dosing. Part 2 is expected to enroll approximately 40 patients with moderate-to-severe AD at up to 12 study centers and will include a preliminary assessment of efficacy. We continue to enroll and dose patients in BBI-02-101 and plan to initiate the MAD part of the study in September 2022. We remain on track to report topline results from the Phase 1 SAD and MAD trials (Parts 1A and 1B) by early 2023. Additionally, we plan to prepare and file an investigational new drug (IND) application with the FDA for further research and development of BBI-02 in the U.S.
BBI-02 is covered by a composition of matter patent issued in the U.S., Japan, China, and other key countries through at least 2038, subject to patent term extensions and adjustments that may be available depending on how this early-stage asset is developed, as well as a pending Patent Cooperation Treaty (“PCT”) application, and other foreign and U.S. applications for BBI-02, as of the date of this Quarterly Report.
BBI-10: A Covalent STING Inhibitor for the Potential Treatment of Autoimmune, Inflammatory, and Rare Genetic Diseases
In February 2022, we entered into an Exclusive License Agreement (the “Carna License Agreement”) with Carna Biosciences, Inc. (“Carna”), pursuant to which we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize Carna’s portfolio of novel, preclinical-stage oral Stimulator of Interferon Genes (“STING”) inhibitors. STING is a well-known mediator of innate immune responses. Excessive signaling through STING is linked to numerous high unmet need diseases, ranging from autoimmune disorders, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, to interferonopathies, which are a set of rare genetic conditions characterized by interferon overproduction and could have orphan drug potential.
STING is a key component of the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (“cGAS”)-STING pathway, which plays an important role in the activation of innate immunity. cGAS acts as a DNA sensor, detecting DNA from sources such as invading bacteria, viruses, and cellular debris that can arise from aging and tissue damage. Upon DNA binding, cGAS produces the secondary messenger molecule cyclic GMP-AMP (“cGAMP”), which binds to STING. STING then undergoes the post-translational modification called palmitoylation, a step essential to the activation of STING. Activated STING then in turn activates the recruitment of kinases that phosphorylate IRF3 and IκBα. Phosphorylated IRF3 leads to activation of the type I interferon response, while phosphorylated IκBα activates NFκB and increases the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFα, resulting in inflammation. While the innate immune response is an important defense mechanism, a dysregulated type I interferon response and overproduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines also represents a driving cause of multiple autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. As such, targeting the cGAS-STING pathway may be a novel approach to treating these diseases.
BBI-10, our lead early-stage STING inhibitor candidate, is a novel, potent, and orally available covalent STING inhibitor that specifically targets the palmitoylation site of STING. This allows it to inhibit both wild-type STING and gain-of-function mutants without competing with cGAMP binding, thus deactivating downstream signaling through IRF3 and IκBα and ultimately suppressing inflammation. BBI-10 has exhibited strong proof-of mechanism and a promising profile in initial pharmacokinetics, toxicology, and safety pharmacology studies. In addition, in vitro studies show that BBI-10 more potently blocks the STING pathway compared to other known STING palmitoylation inhibitors, and that mice treated with BBI-10 demonstrate significant decreases in
pro-inflammatory cytokine production following stimulation of STING. Preclinical development activities for BBI-10 are currently underway, and we expect to conduct experimental characterization of the STING inhibitor library throughout 2022.
For BBI-10, as of the date of this Quarterly Report, we currently have one pending PCT application and one pending priority patent application. We possess an exclusive license directed to a library of compounds targeting/inhibiting STING, pharmaceutical compositions containing the same, and methods of their use, which are being evaluated.
Next-Generation Kinase Inhibitors: A Cutting-Edge Platform with Potential to Produce Treatments for Autoimmune, Inflammatory, and Other Debilitating Diseases
As part of the Voronoi License Agreement, in August 2021 we acquired exclusive global rights to a cutting-edge platform of next-generation kinase inhibitors. This library of new chemical entities includes next-generation DYRK1A inhibitors, as well as other molecules that specifically inhibit CDC2-like kinase (“CLK”), Leucine-Rich Repeat Kinase 2 (“LRRK2”) and TTK protein kinase (“TTK”), also known as Monopolar spindle 1 (Mps1) kinases. A number of these drug candidates have the potential to penetrate the blood brain barrier, presenting an opportunity to address neuroinflammatory conditions of high unmet need such as Down Syndrome, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Parkinson’s Disease, while other peripherally acting novel LRRK2, TTK, and CLK kinase inhibitors could be developed in additional therapeutic areas within autoimmunity, inflammation, and oncology. We are currently engaged in research to identify both brain penetrant and non-brain penetrant new chemical entities from this next-generation kinase inhibitor platform.
Compounds from the next-generation kinase inhibitor platform are covered by U.S. and foreign composition of matter patent applications, as well as other applications, that are currently pending in global prosecution based on our exclusive license from Voronoi related to DYRK1A, LRRK2, TTK, and CLK kinases.
Strategic, Licensing, and Other Arrangements
Exclusive License and Development Agreement with Carna
In February 2022, we entered into the Carna License Agreement with Carna, pursuant to which we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize Carna’s portfolio of novel STING inhibitors. In accordance with the terms of the Carna License Agreement, in exchange for the licensed rights, we made a one-time cash payment of $2.0 million, which was recorded as research and development expenses in the condensed consolidated statements of operations during the six months ended June 30, 2022.
The Carna License Agreement provides that we will make success-based payments to Carna of up to $258.0 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. Further, the Carna License Agreement provides that we will pay Carna tiered royalty payments ranging from mid-single digits up to 10% of net sales. All of the contingent payments and royalties are payable in cash in U.S. Dollars. Under the terms of the Carna License Agreement, we are responsible for, and bear the future costs of, all development and commercialization activities, including patenting, related to all the licensed compounds. As of June 30, 2022 and through the date of this Quarterly Report, we have not yet made any payments or recorded any liabilities related to the specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones or royalties on net sales pursuant to the Carna License Agreement.
License and Development Agreement with Voronoi
In August 2021, we entered into the Voronoi License Agreement with Voronoi, pursuant to which we acquired exclusive, worldwide rights to research, develop, and commercialize BBI-02, a novel, clinical-stage, potential first-in-class, oral DYRK1A inhibitor, and other next-generation kinase inhibitors. In accordance with the terms
of the Voronoi License Agreement, in exchange for the licensed rights, we made a one-time payment of $2.5 million in cash and issued $2.0 million, or 2,816,901 shares, of our common stock to Voronoi.
With respect to BBI-02, the Voronoi License Agreement provides that we will make payments to Voronoi of up to $211.0 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. With respect to the next-generation compounds arising from the novel kinase inhibitor platform, we will make payments to Voronoi of up to $107.5 million in the aggregate contingent upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. Further, the Voronoi License Agreement provides that we will pay Voronoi tiered royalty payments ranging from low-single digits up to 10% of net sales of products arising from the DYRK1A inhibitor programs and next-generation kinase inhibitor platform. All of the contingent payments and royalties are payable in cash in U.S. Dollars, except for $1.0 million of the development and regulatory milestone payments, which amount is payable in equivalent shares of our common stock. Under the terms of the Voronoi License Agreement, we are responsible for, and bear the future costs of, all development and commercialization activities, including patenting, related to all the licensed compounds. As of June 30, 2022 and through the date of this Quarterly Report, we have not yet made any payments or recorded any liabilities related to the specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones or royalties on net sales pursuant to the Voronoi License Agreement.
Asset Purchase Agreement with Botanix
On May 3, 2022 (the “Effective Date”), we and Brickell Subsidiary, Inc. (“Brickell Subsidiary”) entered into an asset purchase agreement with Botanix and Botanix Pharmaceuticals Limited (the “Asset Purchase Agreement”), pursuant to which Botanix acquired and assumed control of all rights, title, and interests to assets primarily related to the proprietary compound sofpironium bromide that were owned and/or licensed by us or Brickell Subsidiary (the “Assets”). We had previously entered into a License Agreement with Bodor Laboratories, Inc. (“Bodor”), dated December 15, 2012 (last amended in February 2020) that provided us with a worldwide exclusive license to develop, manufacture, market, sell, and sublicense products containing sofpironium bromide through which the Assets were developed (the “Amended and Restated License Agreement”). As a result of the Asset Purchase Agreement, Botanix is now responsible for all further research, development, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide globally and replaced us as the exclusive licensee under the Amended and Restated License Agreement.
In accordance with the sublicense rights provided to us under the Amended and Restated License Agreement, we also previously entered into a License, Development, and Commercialization Agreement with Kaken, dated as of March 31, 2015 (as amended in May 2018, the “Kaken Agreement”), under which we granted to Kaken an exclusive right to develop, manufacture, and commercialize the sofpironium bromide compound in Japan and certain other Asian countries (the “Territory”). In exchange for the sublicense, we were entitled to receive aggregate payments of up to $10.0 million upon the achievement of specified development milestones, which was earned and received in 2017 and 2018, and up to $19.0 million upon the achievement of sales-based milestones, as well as tiered royalties based on a percentage of net sales of licensed products in the Territory. In September 2020, Kaken received regulatory approval in Japan to manufacture and market sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (ECCLOCK) for the treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis, and as a result, we began recognizing royalty revenue earned on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK in Japan. Pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Kaken Agreement was also assigned to Botanix, which replaced us as the exclusive sub-licensor to Kaken. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, prior to entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement, we recognized royalty revenue of $0 and $0.2 million, respectively, under the Kaken Agreement. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, we recognized royalty revenue of $0.1 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
We determined that the development of and ultimate sale and assignment of rights to the Assets is an output of our ordinary activities and Botanix is a customer as it relates to the sale of the Assets and related activities.
In accordance with the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement, in exchange for the Assets, we (i) received an upfront payment at closing in the amount of $3.0 million, (ii) are to be reimbursed for certain recent development expenditures in advancement of the Assets, and (iii) will receive from Botanix contingent milestone payments of (a) $2.0 million upon the acceptance by the FDA of the filing of a new drug application (“NDA”) for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, and (b) $4.0 million if marketing approval in the U.S. for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, is received on or before September 30, 2023, or $2.5 million if such marketing approval is received after September 30, 2023 but on or before February 17, 2024. We also are eligible to receive additional success-based regulatory and sales milestone payments of up to $168 million. Further, we will receive tiered earnout payments ranging from high-single digits to mid-teen digits on net sales of sofpironium bromide gel (the “Earnout Payments”).
The Asset Purchase Agreement also provides that Botanix will pay to us a portion of the sales-based milestone payments and royalties that Botanix receives from Kaken under the Kaken Agreement (together, the “Sublicense Income”). During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, we recorded contract revenue for the upfront payment we received from Botanix of $3.0 million, reimbursed development expenditures from Botanix under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.6 million, and fees for consulting services we provided under the TSA (as defined below) of $0.4 million. Additionally, during the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, we recognized contract revenue of $0.3 million related to the Sublicense Income.
All other consideration due under the Asset Purchase Agreement is contingent upon certain regulatory approvals and future sales subsequent to such regulatory approvals or is based upon future sales that we determined are not yet probable due to such revenues being highly susceptible to factors outside of our influence and uncertainty about the amount of such consideration that will not be resolved for an extended period of time. Therefore, we determined that such variable consideration amounts are fully constrained as of June 30, 2022, and, as such, have not yet been recognized as contract revenue.
Transition Services Agreement with Botanix
In connection with the sale of the Assets, on the Effective Date, we and Botanix entered into a transition services agreement (the “TSA”) whereby we are providing consulting services as an independent contractor to Botanix in support of and through filing and potential approval of the U.S. NDA for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%. In accordance with the terms of the TSA, in exchange for providing these services, we will receive from Botanix, (i) prior to the acceptance of the filing by the FDA of such NDA, a fixed monthly amount of $71 thousand, and (ii) after the acceptance of the filing by the FDA of such NDA, a variable amount based upon actual hours worked, in each case plus related fees and expenses of our advisors (plus a 5% administrative fee) and our out-of-pocket expenses. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, we recognized contract revenue of $0.4 million related to these services.
Agreements with Bodor
In connection with the sale of the Assets, on the Effective Date, we, Brickell Subsidiary, and Bodor entered into an agreement (the “Rights Agreement”) to clarify that we and Brickell Subsidiary have the power and authority under the Amended and Restated License Agreement to enter into the Asset Purchase Agreement and the TSA, and that Botanix would assume the Amended and Restated License Agreement pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement. The Rights Agreement includes a general release of claims and no admission of liability between the parties. Pursuant to such Rights Agreement, we have agreed to pay Bodor (i) 18% of the amount of each payment actually received by us from Botanix for upfront and milestone payments under the Asset Purchase Agreement, as well as (ii) certain tiered payments, set as a percentage ranging from mid-single digits to low-teen digits, of the actual amount of each of the applicable Earnout Payments received by us from Botanix. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, we incurred $0.5 million of general and administrative expenses for payments due to Bodor.
Pursuant to the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement, we retained our obligation under the Amended and Restated License Agreement to issue $1.0 million in shares of our common stock to Bodor upon the FDA’s acceptance of an NDA filing for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%. As such regulatory milestone event has not yet been achieved, no research and development expenses associated with milestones were incurred during the three or six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021. Prior to the execution of the Rights Agreement, we paid Bodor immaterial amounts with respect to the royalties we received from Kaken for sales of sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (ECCLOCK) in Japan during those periods.
Nasdaq Listing Matter
As previously disclosed, we received notices of noncompliance with the minimum closing bid price requirement for continued listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market, the most recent of which granted us until June 13, 2022 to regain compliance with that requirement. On June 14, 2022, Nasdaq notified us that we did not regain compliance with the minimum closing bid price requirement as of June 13, 2022, and therefore our common stock would be delisted from The Nasdaq Capital Market, unless we appealed the delisting determination by timely requesting a hearing before the Nasdaq Hearings Panel. We timely requested the hearing, which request stayed any further delisting action, and a hearing was scheduled for July 28, 2022.
On June 30, 2022, our stockholders approved a reverse stock split of our outstanding common stock, which was effected at a split ratio of 1-for-45 on July 5, 2022, at which date each forty-five (45) shares of common stock issued and outstanding immediately prior to the reverse stock split were automatically reclassified, combined and converted into one (1) validly issued, fully paid, and non-assessable share of our common stock, subject to the treatment of fractional share interests. Subsequently, the closing price of our common stock was in excess of $1.00 for 10 consecutive trading days, and on July 19, 2022, we received formal notice from Nasdaq stating that we regained compliance with the minimum closing bid price requirement for continued listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market and, accordingly, the previously-scheduled hearing regarding the delisting action was canceled by Nasdaq and our common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq.
Significant Financing Arrangements
This section sets forth our recent and ongoing financing arrangements, all of which involve our common stock.
Public Offerings of Common Stock and Warrants
In October 2021, we completed the sale of 30,263,400 shares of our common stock (the “October 2021 Offering”). The October 2021 Offering resulted in net proceeds of approximately $10.3 million, after deducting the underwriting discount and offering expenses payable by us.
In July 2021, we completed the sale of 12,983,871 shares of our common stock (the “July 2021 Offering”). The July 2021 Offering resulted in net proceeds of approximately $7.3 million, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by us.
In October 2020, we completed the sale of 19,003,510 shares of our common stock, and, to certain investors, pre-funded warrants to purchase 1,829,812 shares of our common stock, and accompanying common stock warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 20,833,322 shares of our common stock (the “October 2020 Offering”). The October 2020 Offering resulted in net proceeds of approximately $13.7 million to us after deducting underwriting commissions and discounts and other offering expenses payable by us of $1.3 million and excluding the proceeds from the exercise of the warrants. During the six months ended March 31, 2021, 12,427,387 common warrants associated with the October 2020 Offering were exercised at a weighted-average exercise price of $0.72 per share, resulting in aggregate proceeds of approximately $8.9 million.
In June 2020, we completed the sale of 14,790,133 shares of our common stock, and, to certain investors, pre-funded warrants to purchase 2,709,867 shares of our common stock, and accompanying common warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 17,500,000 shares of our common stock (the “June 2020 Offering”). The June 2020 Offering resulted in approximately $18.7 million of net proceeds after deducting underwriting commissions and discounts and other offering expenses payable by us of $1.4 million and excluding the proceeds from the exercise of the warrants. During the six months ended March 31, 2021, 17,500 common warrants associated with the June 2020 Offering were exercised at a weighted-average exercise price of $1.25 per share, resulting in aggregate proceeds of approximately $22 thousand.
We have used and continue to use the remaining net proceeds from our common stock offerings for research and development, including clinical trials, working capital, and general corporate purposes. For additional information regarding the offerings described above, see Note 7. “Capital Stock” of the notes to our condensed consolidated financial statements included in this Quarterly Report.
At Market Issuance Sales Agreements
In March 2021, we entered into an At Market Issuance Sales Agreement (the “2021 ATM Agreement”) with Oppenheimer & Co. Inc. (“Oppenheimer”) and William Blair & Company, L.L.C. (“William Blair”) as our sales agents (the “Agents”). Pursuant to the terms of the 2021 ATM Agreement, we may sell from time to time through the Agents shares of our common stock having an aggregate offering price of up to $50.0 million. Such shares are issued pursuant to our shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-254037). Sales of shares are made by means of ordinary brokers’ transactions on The Nasdaq Capital Market at market prices or as otherwise agreed by us and the Agents. Under the terms of the 2021 ATM Agreement, we may also sell the shares from time to time to an Agent as principal for its own account at a price to be agreed upon at the time of sale. Any sale of the shares to an Agent as principal would be pursuant to the terms of a separate placement notice between us and such Agent. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, we sold 1,419,970 shares of our common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.12 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $0.2 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to the Agents. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, we sold 3,963,476 shares of our common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.89 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $3.4 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to the Agents. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $45.9 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold under the 2021 ATM Agreement. Subsequent to June 30, 2022 and through August 11, 2022, we sold shares of common stock under the 2021 ATM Agreement for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $0.7 million.
In April 2020, we entered into an At Market Issuance Sales Agreement (the “2020 ATM Agreement” and, together with the 2021 ATM Agreement, the “ATM Agreements”) with Oppenheimer as our sales agent. Pursuant to the terms of the 2020 ATM Agreement, we may sell from time to time through Oppenheimer shares of our common stock having an aggregate offering price of up to $8.0 million. Such shares are issued pursuant to our shelf registration statement on Form S-3 (Registration No. 333-236353). Sales of the shares are made by means of ordinary brokers’ transactions on The Nasdaq Capital Market at market prices or as otherwise agreed by us and Oppenheimer. Under the terms of the 2020 ATM Agreement, we may also sell the shares from time to time to Oppenheimer as principal for its own account at a price to be agreed upon at the time of sale. Any sale of the shares to Oppenheimer as principal would be pursuant to the terms of a separate placement notice between us and Oppenheimer. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, no sales of common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement occurred. During the three months ended June 30, 2021, we sold 5,500 shares of our common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $1.16 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $6.2 thousand, after giving effect to a 3% commission to Oppenheimer as agent. During the six months ended June 30, 2021, we sold 1,089,048 shares of our common stock under the 2020 ATM Agreement at a weighted-average price of $1.55 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of approximately $1.6 million, after giving effect to a 3% commission to Oppenheimer as agent. As of June 30,
2022, approximately $2.6 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold under the 2020 ATM Agreement.
We are subject to the SEC’s “baby shelf rules,” which prohibit companies with a public float of less than $75 million from issuing securities under a shelf registration statement in excess of one-third of such company’s public float in a 12-month period. These rules may limit future issuances of shares by us under the ATM Agreements or other common stock offerings.
Private Placement Offerings
In February 2020, we and Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“Lincoln Park”) entered into (i) a securities purchase agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”); (ii) a purchase agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”); and (iii) a registration rights agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”). Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, Lincoln Park purchased, and we sold, (i) an aggregate of 950,000 shares of common stock (the “Common Shares”); (ii) a warrant to initially purchase an aggregate of up to 606,420 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $0.01 per share (the “Series A Warrant”); and (iii) a warrant to initially purchase an aggregate of up to 1,556,420 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $1.16 per share (the “Series B Warrant” and, together with the Series A Warrant, the “Warrants”). The aggregate gross purchase price for the Common Shares and the Warrants was $2.0 million.
Under the terms and subject to the conditions of the Purchase Agreement, we have the right, but not the obligation, to sell to Lincoln Park, and Lincoln Park is obligated to purchase, up to $28.0 million in the aggregate of shares of our common stock. In order to retain maximum flexibility to issue and sell up to the maximum of $28.0 million of our common stock under the Purchase Agreement, we sought and, at our annual meeting on April 19, 2021, received, stockholder approval for the sale and issuance of common stock in connection with the Purchase Agreement under Nasdaq Listing Rule 5635(d). Sales of common stock by us will be subject to certain limitations, and may occur from time to time, at our sole discretion, over the 36-month period commencing on August 14, 2020 (the “Commencement Date”).
Following the Commencement Date, under the Purchase Agreement, on any business day selected by us, we may direct Lincoln Park to purchase up to 100,000 shares of our common stock on such business day (each, a “Regular Purchase”), provided, however, that (i) the Regular Purchase may be increased to up to 125,000 shares, provided that the closing sale price of the common stock is not below $3.00 on the purchase date; and (ii) the Regular Purchase may be increased to up to 150,000 shares, provided that the closing sale price of the common stock is not below $5.00 on the purchase date. In each case, Lincoln Park’s maximum commitment in any single Regular Purchase may not exceed $1,000,000. The purchase price per share for each such Regular Purchase will be based on prevailing market prices of common stock immediately preceding the time of sale. In addition to Regular Purchases, we may direct Lincoln Park to purchase other amounts as accelerated purchases or as additional accelerated purchases if the closing sale price of the common stock exceeds certain threshold prices as set forth in the Purchase Agreement. In all instances, we may not sell shares of our common stock to Lincoln Park under the Purchase Agreement if it would result in Lincoln Park beneficially owning more than 9.99% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2022, no sales of common stock under the Purchase Agreement occurred. During the three and six months ended June 30, 2021, we sold to Lincoln Park 800,000 shares under the Purchase Agreement at a weighted-average price of $0.81 per share, for aggregate net proceeds of $0.6 million. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $26.9 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold under the Purchase Agreement. However, only 57,751 of such shares (less than $175,000 of shares assuming a sale date of August 11, 2022) have been registered by us under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”).
We agreed with Lincoln Park that we will not enter into any “variable rate” transactions with any third party, subject to certain exceptions, for a period defined in the Purchase Agreement. We have the right to terminate the Purchase Agreement at any time, at no cost or penalty.
Financial Overview
Our operations to date have been limited to business planning, raising capital, developing and entering into strategic partnerships for our pipeline assets, identifying and in-licensing product candidates, conducting clinical trials, and other research and development activities.
To date, we have financed operations primarily through funds received from the sale of common stock and warrants, convertible preferred stock, debt and convertible notes, and payments received under license, collaboration, and other agreements. Other than through arrangements as they relate to sales of ECCLOCK in Japan, none of our product candidates has been approved for sale and we have not generated any product sales. Since inception, we have incurred operating losses. We recorded a net loss of $10.6 million and $20.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, respectively. As of June 30, 2022, we had an accumulated deficit of $155.9 million. We expect to continue incurring significant expenses and operating losses for at least the next several years as we:
•execute a Phase 1 clinical trial, along with other nonclinical development activities, for BBI-02;
•conduct preclinical development activities for BBI-10 and experimental characterization of the STING inhibitor library;
•engage in research to identify both brain penetrant and non-brain penetrant kinase inhibitors from the next-generation kinase inhibitor platform;
•advance research and development-related activities to develop and expand our product pipeline;
•maintain, expand, and protect our intellectual property portfolio for all our assets;
•hire additional staff, including clinical, regulatory, quality, program and alliance management, scientific, and management personnel; and
•add operational and finance personnel to support product and business development efforts.
We do not expect to generate significant revenue unless and until we successfully complete development of, obtain marketing approval for, and commercialize product candidates, either alone or in collaboration with third parties. We expect these activities may take several years and our success in these efforts is subject to significant uncertainty. We expect we will need to raise substantial additional capital prior to the regulatory approval and commercialization of any of our product candidates. Until such time, if ever, that we generate substantial product revenue, we expect to finance our operations through public or private equity or debt financings, collaborations or licenses, or other available financing transactions. However, we may be unable to raise additional funds through these or other means when needed.
Key Components of Operations
Revenue
Revenue generally consists of revenue recognized under our strategic agreements for the development and commercialization of our product candidates. Our strategic agreements generally outline overall development plans and include payments we receive at signing, payments for the achievement of certain milestones, sublicense income, earnout payments on net product sales, and royalties on net product sales. For these activities and payments, we utilize judgment to assess the nature of the performance obligations to determine whether the performance obligations are satisfied over time or at a point in time and, if over time, the appropriate method of measuring progress for purposes of recognizing revenue. Prior to entering into the Asset
Purchase Agreement, we recognized royalty revenue earned on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK in Japan. Beginning in the second quarter of 2022, we began recognizing contract revenue pursuant to the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement. Other than the contract revenue we may generate in connection with the Asset Purchase Agreement, we do not expect to generate any revenue from any product candidates that we developed or develop unless and until we obtain regulatory approval and commercialize our products or enter into other collaboration agreements with third parties.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses principally consist of payments to third parties known as clinical research organizations (“CROs”) and upfront in-licensing fees of development-stage assets. CROs help plan, organize, and conduct clinical and nonclinical studies under our direction. Personnel costs, including wages, benefits, and share-based compensation, related to our research and development staff in support of product development activities are also included, as well as costs incurred for supplies, clinical and nonclinical studies, consultants, and facility and related overhead costs.
Below is a summary of our research and development expenses related to our programs by categories of costs for the periods presented.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended
June 30, | | Six Months Ended
June 30, | | |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | 2022 | | 2021 | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Direct program expenses related to | | | | | | | | | |
| Sofpironium bromide (1) | $ | — | | | $ | 8,114 | | | $ | 2,090 | | | $ | 13,550 | | | |
| DYRK1A inhibitor program (2) | 958 | | | — | | | 1,686 | | | — | | | |
| STING inhibitor program (3) | 28 | | | — | | | 2,038 | | | — | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Personnel and other expenses (4) | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, benefits, and stock-based compensation | 741 | | | 460 | | | 1,493 | | | 936 | | | |
| Regulatory and compliance | 103 | | | 244 | | | 384 | | | 371 | | | |
| Other expenses | 35 | | | 20 | | | 187 | | | 33 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total research and development expenses | $ | 1,865 | | | $ | 8,838 | | | $ | 7,878 | | | $ | 14,890 | | | |
____________
(1)Sofpironium bromide. Expenses associated with sofpironium bromide decreased in the three and six months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the three and six months ended June 30, 2021 as Phase 3 clinical trials were completed in the fourth quarter of 2021. We do not expect to incur any additional research and development expenses related to sofpironium bromide subsequent to the Effective Date, when we sold the assets primarily related to sofpironium bromide that we previously owned and/or licensed to Botanix, which is responsible for all further research, development, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide.
(2)DYRK1A inhibitor program. As part of our potential first-in-class DYRK1A inhibitor program targeting autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, we initiated a Phase 1 clinical trial for BBI-02, our lead DYRK1A inhibitor candidate, in Canada in the second quarter of 2022 that we expect will continue through early 2023. We are also engaged in research to identify new chemical entities from our next-generation kinase inhibitor platform. As a result, in the following years, we expect to incur
research and development expenses for these programs at levels consistent with expenditures for development of early-stage assets.
(3)STING inhibitor program. In February 2022, we acquired a portfolio of novel, potent, and orally available STING inhibitors that has broad potential in autoinflammatory diseases. To date, the expenses associated with our STING inhibitor program primarily relate to upfront in-licensing fees. Nonclinical development activities for our lead early-stage STING inhibitor candidate, BBI-10, are currently underway, and we expect to conduct experimental characterization of the STING inhibitor library throughout 2022. As a result, in the following years, we expect to incur research and development expenses for this program at levels consistent with expenditures for development of early-stage assets.
(4)Personnel and other expenses. Personnel and other expenses include operational expenses related to research and development activities not specifically attributable to a specific program. Other expenses include travel, lab and office supplies, clinical trial management software, license fees, and other miscellaneous expenses.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel costs, including wages, benefits, and share-based compensation, related to our executive, sales, marketing, finance, and human resources personnel, as well as professional fees, including legal, accounting, and sublicensing fees.
Critical Accounting Estimates
We have prepared the condensed consolidated financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The preparation of these condensed consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates, assumptions, and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, and related disclosures at the date of the condensed consolidated financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. On an ongoing basis, management evaluates its critical estimates, including those related to revenue recognition and accrued research and development expenses. We base our estimates on our historical experience and on assumptions that we believe are reasonable; however, actual results may differ materially from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
During the three months ended June 30, 2022, we identified the following to be an additional critical accounting estimate because it is both important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and requires critical judgment by management and estimates about matters that are uncertain.
Contract Revenue Recognition
Pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement described in Note 3. “Strategic Agreements,” we have rights to receive from Botanix future milestone payments, sales-based payments, and sublicense income related to sales-based milestones and royalties earned by Botanix from Kaken under the Kaken Agreement (all of such payments, “Botanix Payments”). The payments under the Asset Purchase Agreement vary based on net sales and/or are contingent upon certain regulatory approvals. Therefore, we are required to estimate the Botanix Payments, which represent variable consideration, to be achieved and recognize revenue to the extent it is probable that a significant reversal in the amount of cumulative revenue recognized will not occur. We may use either the most likely amount or the expected value method in making such estimates based on the nature of the payment to be received and whether there is a wide range of outcomes or only two possible outcomes. For any milestone payments, we utilize the most likely amount method, which represents our best estimate of the single most likely outcome to be achieved. For any royalty-based payments or other consideration where there are
more than two possible outcomes, we utilize the expected value method, which represents the sum of probability-weighted amounts in a range of possible consideration amounts.
We base our estimates of variable consideration to be recognized as revenue using the applicable method described above on factors such as, but not limited to, required regulatory approvals, historical sales levels, market events and projections, and others as necessary. We update our estimates at each reporting period based on actual results and future expectations as necessary. Our estimates are subject to changes in net sales of sofpironium bromide and the occurrence of contingent events, such as regulatory approvals. Changes in net sales could occur due to various risks such as competitors entering the market, technology changes as to how hyperhidrosis is treated, and foreign exchange risk.
Except for the critical accounting estimates associated with the contract revenue recognition described above, there were no changes during the six months ended June 30, 2022 to our critical accounting estimates as disclosed in our 2021 Annual Report on Form 10-K. For information on our significant accounting policies, please refer to Note 2 of the notes to our condensed consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Quarterly Report.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
We believe that the impact of recently issued guidance, whether adopted or to be adopted in the future, is not expected to have a material impact on our condensed consolidated financial statements upon adoption.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Three Months Ended June 30, 2022 and 2021
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended
June 30, | | |
| 2022 | | 2021 | | | | |
| (in thousands) | | | | |
| Revenue | $ | 4,315 | | | $ | 151 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | (1,865) | | | (8,838) | | | | | |
| General and administrative expenses | (3,908) | | | (2,891) | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total other income, net | 311 | | | 429 | | | | | |
| Net loss | $ | (1,147) | | | $ | (11,149) | | | | | |
Revenue
Revenue increased by $4.2 million for the three months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2021. Revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2022 consisted of contract revenue recognized under the Asset Purchase Agreement and TSA with Botanix, while revenue for the three months ended June 30, 2021 was driven by royalty revenue earned on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK in Japan under the Kaken Agreement. Upon entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement on the Effective Date, whereby we sold all rights, title, and interests to assets primarily related to sofpironium bromide that were owned and/or licensed by us, and through June 30, 2022, we recognized contract revenue that was associated with the following: an upfront payment from Botanix of $3.0 million; reimbursed development expenditures from Botanix under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.6 million; fees for consulting services we provided under the TSA of $0.4 million; and Sublicense Income under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.3 million. We expect contract revenue associated with services we provide under the TSA to continue through the date the FDA issues a final decision on the NDA that will be submitted for sofpironium bromide gel. After June 30,
2022, we expect to continue to recognize contract revenue related to royalties on applicable net sales of sofpironium bromide gel pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement, as such estimated sales become probable.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses decreased by $7.0 million for the three months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2021, which was driven primarily by lower clinical expenses of $8.1 million related to sofpironium bromide, partially offset by increased clinical costs of $1.0 million for BBI-02. Throughout 2021, we were executing a U.S. Phase 3 pivotal clinical program for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, which concluded in the fourth quarter of 2021. During the second quarter of 2022, we initiated our Phase 1 clinical trial for BBI-02 and began incurring research and develop expenses related to the clinical trial.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $1.0 million for the three months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2021. The increase was primarily related to expenses incurred in the second quarter of 2022 for a $0.5 million payment to Bodor under the Rights Agreement and higher expenses associated with legal and compliance fees of $0.3 million, compensation-related expenses of $0.1 million, and other administrative fees $0.1 million.
Total Other Income, Net
Total other income, net decreased by $0.1 million for the three months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2021. The decrease was primarily due to a gain on extinguishment of debt of approximately $0.4 million during the three months ended June 30, 2021 that resulted from the forgiveness of an outstanding loan that we received under the Paycheck Protection Program (the “PPP Loan”) in June 2021, partially offset by $0.3 million of liabilities assumed by Botanix related to development costs during the three months ended June 30, 2022 prior to the Effective Date.
Comparison of the Six Months Ended June 30, 2022 and 2021
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| | | | | 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | | | (in thousands) |
| Revenue | | | | | $ | 4,407 | | | $ | 168 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | | | | (7,878) | | | (14,890) | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | | | (7,394) | | | (5,858) | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total other income, net | | | | | 308 | | | 426 | |
| Net loss | | | | | $ | (10,557) | | | $ | (20,154) | |
Revenue
Revenue increased by $4.2 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021. Revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2022 primarily consisted of contract revenue recognized under the Asset Purchase Agreement and TSA with Botanix, while revenue for the six months ended June 30, 2021 was driven by royalty revenue earned on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK in Japan under the Kaken Agreement. Upon entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement on the Effective Date, whereby we sold all rights, title, and interests to assets primarily related to sofpironium bromide that were owned and/or licensed by us, and through June 30, 2022, we recognized contract revenue that was associated with the following: an upfront payment from Botanix of $3.0 million; reimbursed development expenditures from
Botanix under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.6 million; fees for consulting services we provided under the TSA of $0.4 million; and Sublicense Income under the Asset Purchase Agreement of $0.3 million. We expect contract revenue associated with services we provide under the TSA to continue through the date the FDA issues a final decision on the NDA that will be submitted for sofpironium bromide gel. After June 30, 2022, we expect to continue to recognize contract revenue related to royalties on applicable net sales of sofpironium bromide gel pursuant to the Asset Purchase Agreement, as such estimated sales become probable.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses decreased by $7.0 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022, compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021, driven primarily by lower clinical expenses of $11.5 million related to sofpironium bromide, partially offset by upfront costs of $2.0 million incurred for the acquisition of our STING inhibitor platform in February 2022, increased clinical costs of $1.7 million for BBI-02, and increased costs of $0.8 million related to personnel and other expenses. Throughout 2021, we were executing our U.S. Phase 3 pivotal clinical program for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, which concluded in the fourth quarter of 2021. During the second quarter of 2022, we initiated our Phase 1 clinical trial for BBI-02 and began incurring research and development expenses related to the clinical trial.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $1.5 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022, compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021. The increase was primarily related to expenses incurred in the six months ended June 30, 2022 for a $0.5 million payment to Bodor under the Rights Agreement and higher expenses associated with legal and compliance fees of $0.5 million, compensation-related expenses of $0.3 million, and other administrative expenses of $0.2 million.
Total Other Income, Net
Total other income, net decreased by $0.1 million for the six months ended June 30, 2022 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021. The decrease was primarily due to a gain on extinguishment of debt of approximately $0.4 million that resulted from the forgiveness of the PPP Loan in June 2021, partially offset by $0.3 million of liabilities assumed by Botanix related to development costs during the six months ended June 30, 2022 prior to the Effective Date.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have incurred significant operating losses and have an accumulated deficit as a result of ongoing efforts to in-license and develop our product candidates, including conducting preclinical and clinical trials and providing general and administrative support for these operations. For the six months ended June 30, 2022 and 2021, we had a net loss of $10.6 million and $20.2 million, respectively. As of June 30, 2022, we had an accumulated deficit of $155.9 million. As of June 30, 2022, we had cash and cash equivalents of $14.5 million compared to $26.9 million as of December 31, 2021. Since inception, we have financed our operations primarily through funds received from the sale of common stock and warrants, convertible preferred stock, debt, and convertible notes, and payments received under license and strategic agreements.
We believe that our cash and cash equivalents as of June 30, 2022, combined with $2.0 million from expected near-term payments under the Asset Purchase Agreement, will be sufficient to fund our operations for at least the next 12 months. However, it is difficult to predict our spending for our product candidates prior to obtaining FDA approval. Moreover, changing circumstances may cause us to expend cash significantly faster than we currently anticipate, and we may need to spend more cash than currently expected because of circumstances beyond our control. We expect to continue to incur additional substantial losses in the foreseeable future as a result of our research and development activities. Additional funding will be required in the future to continue
with our planned development and other activities. However, we may be unable to raise additional funds, which would have a negative impact on our business, financial condition, and our ability to develop our pipeline. To the extent that additional funds are raised through the sale of equity, the issuance of securities will result in dilution to our stockholders.
Additionally, we are subject to the SEC’s “baby shelf rules,” which prohibit companies with a public float of less than $75 million from issuing securities under a shelf registration statement in excess of one-third of such company’s public float in a 12-month period. These rules may limit our future issuances of shares under the ATM Agreements or other common stock offerings.
Cash Flows
Since inception, we have primarily used our available cash to fund expenditures related to product discovery and development activities. The following table sets forth a summary of cash flows for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Six Months Ended
June 30, |
| 2022 | | 2021 |
| | | |
| | | |
| (in thousands) |
| Net cash provided by (used in): | | | |
| Operating activities | $ | (12,509) | | | $ | (20,205) | |
| Investing activities | — | | | (36) | |
| Financing activities | 105 | | | 14,534 | |
| Total | $ | (12,404) | | | $ | (5,707) | |
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities of $12.5 million during the six months ended June 30, 2022 decreased compared to $20.2 million during the six months ended June 30, 2021, which was primarily attributable to a decrease in cash used to support our operating activities, including but not limited to, our clinical trials, research and development activities, and general working capital requirements. The $7.7 million decrease was impacted by the net effect of a decrease in net loss of $9.6 million and an increase in non-cash operating expenses of $0.7 million, partially offset by the net effect of changes in working capital of $2.6 million.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities during the six months ended June 30, 2022 decreased by $36 thousand compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021, due to the fact that we did not purchase any property and equipment in the current year period.
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities during the six months ended June 30, 2022 decreased by $14.4 million compared to the six months ended June 30, 2021. The decrease primarily resulted from net proceeds received during the six months ended June 30, 2021 of $9.0 million from the exercise of warrants and a reduction during the six months ended June 30, 2022 of $5.4 million in proceeds from sales of our common stock under the 2020 and 2021 ATM Agreements.
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are a smaller reporting company as defined by Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), and are not required to provide the information under this item.
ITEM 4. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures.
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, we conducted an evaluation of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) promulgated under the Exchange Act, as of the end of the period covered by this Quarterly Report. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective and were operating at a reasonable assurance level as of June 30, 2022.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management has determined that there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the three months ended June 30, 2022 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
PART II. OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
From time to time, we may become involved in legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of our business. We are not presently a party to any legal proceedings that, if determined adversely to us, would individually or taken together have a material adverse effect on our company, nor is any such litigation threatened as of the date of this filing.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Our business, financial condition, and operating results may be affected by a number of factors, whether currently known or unknown, including but not limited to those described below. Any one or more of such factors could directly or indirectly cause our actual results of operations and financial condition to vary materially from past or anticipated future results of operations and financial condition. Any of these factors, in whole or in part, alone or combined with any of the other factors, could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, and stock price. The following information should be read in conjunction with Part I, Item 2, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the condensed consolidated financial statements and related notes in Part I, Item 1, “Financial Statements” of this Quarterly Report.
Risks Related to Our Business Operations
Our business depends on the successful continued financing, nonclinical and clinical development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of our pipeline assets.
The successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of our pipeline assets will require significant additional financing and depend on a number of factors, including but not limited to the following:
•timely and successful initiation and completion of clinical trials for our product candidate portfolio, which may be significantly costlier than we currently anticipate and/or produce results that do not achieve the endpoints of the trials, or which are ultimately deemed not to be clinically meaningful;
•our ability to receive regulatory approval for our clinical trials;
•achieving and maintaining, and, where applicable, ensuring that our third-party contractors achieve and maintain, compliance with our and their contractual obligations and with all regulatory and legal requirements applicable to them and to our pipeline assets;
•ability of third parties with which we contract to manufacture consistently adequate clinical trial supplies for development of our pipeline assets, to remain in good standing with regulatory agencies and to develop, validate, and maintain or supervise commercially viable manufacturing processes that are compliant with FDA-regulated current good manufacturing practice (“cGMP”) and other applicable legal requirements, to hire and retain a sufficient and qualified workforce, and to manage their own supply chain(s) to comply with their contractual obligations to us, which supply chains and workforce availability could continue to be constrained during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic;
•a continued acceptable safety and tolerability profile during clinical development of our pipeline assets;
•acceptance by physicians, insurers and payors, and patients of the quality, benefits, safety, and efficacy of our pipeline assets, if and where approved, including relative to alternative and competing treatments and the next best standard of care;
•existence of a regulatory, pricing and reimbursement, and legal environment conducive to the success of our pipeline assets;
•ability to price our pipeline assets to recover our development costs and generate a satisfactory profit margin;
•the ability of third parties to whom we have sold assets or rights to assets to successfully commercialize those assets, including sofpironium bromide, and the resulting impact on our potential future revenue;
•our ability and our partners’ ability to establish, maintain, and enforce intellectual property rights in and to our pipeline assets, including but not limited to patents, regulatory exclusivity rights, trademarks, copyrights, and licenses;
•our ability to raise capital to commercialize and advance our pipeline assets, which will be limited if our common stock price does not appreciate;
•our success in providing Botanix certain contracted-for services in Botanix’s further development of sofpironium bromide, which will trigger future conditional cash payments depending on the level of success in development; and
•the extent to which Botanix is successful in meeting its contract obligations to its licensor and completing the development and commercial launch of sofpironium bromide outside of Japan.
If we do not achieve one or more of these factors, many of which are beyond our reasonable control, in a timely manner or at all, we could experience significant delays, an inability to fund our operations and research and development, or an inability to obtain regulatory approvals or commercialize our pipeline assets.
Even if regulatory approvals are obtained, we may never be able to successfully commercialize our pipeline assets, especially if we attempt to do so without a partner. Accordingly, we cannot assure that we will be able to launch a product candidate in any market or, if we do, that we will be able to generate sufficient revenue from the sale of such product candidate, or any other asset, to continue our business.
Clinical drug development for our pipeline assets is expensive, time-consuming, and uncertain. Any data resulting from our trials may not be favorable for further development.
Clinical development for our pipeline assets is expensive, time-consuming, difficult to design and implement, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Most product candidates that commence clinical trials are never approved by regulatory authorities for commercialization, and of those that are approved, many do not cover their costs of development or ever generate a profit. In addition, we, any partner with which we currently or may in the future collaborate, the FDA, a local or central institutional review board, or other regulatory authorities, including state and local agencies and counterpart agencies in foreign countries, may suspend, delay, extend, require modifications, or add additional requirements to or terminate our clinical trials at any time.
Our pipeline assets primarily target autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, and it is still too early in clinical development to know whether they will progress past Phase 1 clinical trials. Any data resulting from our trials may not be favorable for further development.
Major public health issues, and specifically the pandemic and related impacts caused by the ongoing spread of COVID-19 and COVID-19 variants, including in terms of constraints on supply chains and human resource availability, could have an adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations and other aspects of our business and that of our suppliers, contractors, and business partners.
The extent to which COVID-19 impacts our business and operating results will depend on future developments that are highly uncertain and cannot be accurately predicted, including any new information that may emerge on COVID-19 variants and the actions to contain COVID-19 or treat its impact, especially for variants, among others, how long it takes for global supply chains to handle the pent-up demand for goods and services and the shutdowns associated around the world with those supply chains, and worker eagerness to return to the workforce and/or change employment patterns.
The effects of the COVID-19 pandemic could delay or interrupt our business operations. Ongoing materials required for an eventual NDA for submission to the FDA, study monitoring, and data analysis may be paused or delayed due to changes in hospital or university policies, federal, state, or local regulations, prioritization of hospital resources toward pandemic efforts, worker and supplier patterns, or other reasons related to, or as a consequence of, the pandemic. Some participants and clinical investigators may not be able to comply with clinical trial protocols. For example, quarantines or other travel limitations (whether voluntary or required) may impede participant movement, affect sponsor access to study sites, or interrupt healthcare services, and we may be unable to complete our clinical trials. Further, if our operations are adversely impacted, we risk a delay, default, and/or nonperformance under existing agreements, which may increase our costs. These cost increases may not be fully recoverable or adequately covered by insurance. Infections and deaths related to the pandemic may disrupt the U.S.’ and other countries’ healthcare and healthcare regulatory systems. Such disruptions could divert healthcare resources away from, or materially delay FDA or other regulatory review and/or approval with respect to, our clinical trials. It is unknown how long these disruptions could continue, were they to occur. Any elongation or de-prioritization of our clinical trials or delay in regulatory review resulting from such disruptions could materially affect the development and study of our product candidates.
We currently rely on third parties, such as contract laboratories, contract research organizations, medical institutions, and clinical investigators to conduct studies and clinical trials for our pipeline assets. If these third parties themselves are adversely impacted by restrictions or disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, we will likely experience delays, and/or realize additional costs. As a result, our efforts to obtain regulatory approvals for, and to commercialize, our therapeutic candidates may be delayed or otherwise adversely impacted.
The spread of COVID-19 and its variants, which has caused a broad impact globally, including restrictions on travel and quarantine policies put into place by businesses and governments, negative supply chain impacts, and worker unavailability, may have a material economic effect on our business. While the potential economic impact brought by, and the duration of, the pandemic may be difficult to assess or predict, it has already caused, and is likely to result in further, significant disruption of global financial and distribution markets, which may reduce our ability to access capital either at all or on favorable terms. In addition, a recession, depression, or other sustained adverse market event resulting from the spread of COVID-19 could materially and adversely affect our business and the value of our common stock.
Beginning in March 2022, a stringent lockdown in Shanghai by the Chinese government as a result of rising COVID-19 cases delayed the delivery of materials necessary for our Phase 1 trial for BBI-02. While we received the materials necessary to initiate our Phase 1 trial for BBI-02 on our anticipated timeline, there is no assurance that additional lockdowns, or other related uncertain or unforeseen events caused by this ongoing pandemic, either in China or elsewhere, will not result in delays of any materials or services that may be required for any future research and development activities.
The ultimate impact of this pandemic, or any other health epidemic, continues to be highly uncertain and subject to change. We cannot predict the full extent of potential delays or impacts on our business and that of our key partners, our clinical trials, our research programs, healthcare systems, or the global economy as a whole. However, these effects could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows.
Our product candidates may not achieve adequate market acceptance among physicians, patients, healthcare payors and others in the medical community necessary for commercial success.
Even if our product candidates receive regulatory approval, they may not gain adequate market acceptance among physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community. The degree of market acceptance of any of our approved product candidates will depend on a number of factors, including:
•the efficacy and safety profile as demonstrated in clinical trials compared to alternative treatments;
•the timing of market introduction of the product candidate as well as competitive products;
•the clinical indications for which a product candidate is approved;
•restrictions on the use of product candidates in the labeling approved by regulatory authorities, such as boxed warnings or contraindications in labeling, or a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy, if any, which may not be required of alternative treatments and competitor products;
•the potential and perceived advantages of our product candidates over alternative treatments;
•the cost of treatment in relation to alternative treatments;
•the availability of an approved product candidate for use as a combination therapy;
•relative convenience and ease of administration;
•the willingness of the target patient population or their caregivers to try new therapies and of physicians to prescribe these therapies;
•the availability of coverage and adequate reimbursement by third-party payors, including government authorities;
•patients’ willingness to pay for these therapies in the absence of such coverage and adequate reimbursement;
•the effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts;
•support from key opinion leaders and patient advocacy groups;
•unfavorable publicity relating to our product candidates; and
•the approval of other new therapies for the same indications.
If any of our product candidates are approved but do not achieve an adequate level of acceptance by physicians, hospitals, healthcare payors and patients, we may not generate or derive sufficient revenue from that product candidate and our financial results could be negatively impacted.
We face significant competition in our industry, and our pipeline assets, if approved, may not be able to compete effectively or achieve significant market penetration.
The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition, less effective patent terms, and a strong emphasis on developing newer, fast-to-market proprietary therapeutics. Numerous companies are engaged in the development, patenting, manufacturing, and marketing of healthcare products competitive with those that we are developing. We face competition from a number of sources, such as pharmaceutical companies, generic drug companies, biotechnology companies, and academic and research institutions, many of which have greater financial resources, marketing capabilities, sales forces, manufacturing capabilities, research and development capabilities, regulatory expertise, clinical trial expertise, intellectual property portfolios, more international reach, experience in obtaining patents and regulatory approvals for product candidates and other resources than us. Some of the companies that offer competing products also have a broad range of other product offerings, large direct sales forces, and long-term customer relationships with our target physicians, which could inhibit our market penetration efforts.
To compete successfully, we will have to provide an attractive and cost-effective alternative to existing and new therapies. Such competition could lead to reduced market share and contribute to downward pressure on the pricing of eventual product candidates, which could harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
If CROs and other third parties do not meet our requirements or otherwise conduct clinical trials for our pipeline assets as required or are unable to staff or supply our trials, we may not be able to satisfy our contractual obligations or obtain regulatory approval for, or commercialize, our pipeline assets at all or in the time frames currently planned for.
We have in the past relied, and expect to continue to rely, on third-party CROs to conduct and oversee our clinical trials for pipeline assets and other aspects of product development. We also rely on various medical institutions, clinical investigators, and contract laboratories to conduct our trials in accordance with our clinical protocols and all applicable regulatory requirements, including the FDA’s regulations and good clinical practice (“GCP”) requirements, which are an international standard meant to protect the rights and health of patients and to define the roles of clinical trial sponsors, administrators and monitors, and state regulations governing the handling, storage, security and recordkeeping for drug and biologic products. These CROs and other third parties play a significant role in the conduct of these trials and the subsequent collection and analysis of data from the clinical trials. We rely heavily on these parties for the execution of our clinical trials and preclinical studies and control only certain aspects of their activities. We and our CROs and other third-party contractors are required to comply with GCP and current good laboratory practice (“GLP”) requirements, which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Regulatory authorities enforce these GCP and GLP requirements through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators, and trial sites. If we or any of these third parties fail to comply with applicable GCP and GLP requirements, or reveal noncompliance from an audit or inspection, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or other regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our or our partners’ marketing applications. We cannot assure that upon inspection by a given regulatory authority, such regulatory authority will determine that any of our clinical or preclinical trials comply with applicable GCP and GLP requirements, or that our CROs and other third-party contractors are otherwise compliant with applicable laws despite their contractual assurances to us. In addition, our clinical trials generally must be conducted with product produced under cGMP regulations. Our failure, or the failure of our CROs and other third-party contractors, to comply with these regulations and policies, or to obtain supply of key items in sufficient quantities, in a timely manner or at all, may require us to extend or repeat clinical trials, which would delay or halt the regulatory approval process, or could cause us to fail to meet certain contractual obligations, including but not limited to milestone commitments, with licensors of our portfolio assets like Voronoi and Carna.
If any of our CROs or clinical trial sites terminate their involvement in one of our clinical trials for any reason, including but not limited to impacts caused by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, we may not be able to enter into arrangements with alternative CROs or clinical trial sites, or do so on commercially reasonable terms, and in a satisfactory timeframe. If our relationship with clinical trial sites is terminated, we may experience the loss of follow-up information on patients enrolled in our clinical trials unless we are able to transfer the care of those patients to another qualified clinical trial site. In addition, principal investigators for our clinical trials may serve as scientific advisors or consultants to us from time to time and could receive cash or equity compensation in connection with such services. If these relationships and any related compensation result in perceived or actual conflicts of interest, the integrity of the data generated at the applicable clinical trial site may be questioned by the FDA.
If we do not achieve our projected development goals in the timeframes we announce and expect, our business and strategies may be adversely affected and, as a result, our stock price may decline.
From time to time, we estimate the timing of the anticipated accomplishment of various scientific, clinical, regulatory, other product development, and commercial goals, as well as achievement of certain contractual milestones by us and our partners. These goals may include the commencement or completion of scientific studies and clinical trials and the submission of regulatory filings, as well as product launch. From time to time, we may publicly announce the expected timing of some of these goals. All of these goals are and will be based on numerous assumptions. The actual timing of these goals can vary dramatically compared to our estimates, in some cases for reasons beyond our control or that cannot be anticipated. If we do not meet these goals as publicly announced, or at all, our business and strategies may be adversely affected and, as a result, our stock price may decline.
Our receipt of future payments from Botanix is contingent on various factors outside of our control, including the successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, by Botanix outside of Japan, the successful continued commercialization of sofpironium bromide gel, 5% (ECCLOCK) by Kaken in Japan, and the sufficiency of funds by both entities to pay us and Bodor, the licensor of this product.
Our receipt of future regulatory and sales milestone payments, as well as earnout payments, from Botanix is contingent on the successful development, regulatory approval, and commercialization of sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, which in turn depends on a number of factors, including but not limited to the following:
•whether Botanix is required to conduct additional clinical trials to support its submission of an NDA with the FDA for sofpironium bromide;
•whether Kaken is able to execute successfully, in a timely, compliant, and efficient manner, certain active pharmaceutical ingredient (“API”)-related activities (chemistry, manufacturing, and controls) that Botanix is reliant on in connection with FDA approval in the U.S.;
•whether Kaken is able to satisfy its requirement to provide Botanix with certain key regulatory information that will be used for its NDA submission to the FDA for sofpironium bromide;
•if approved, the ability to manufacture consistently adequate commercial supplies of sofpironium bromide, to remain in good standing with regulatory agencies and to develop, validate, and maintain or supervise commercially viable manufacturing processes that are compliant with FDA-regulated cGMPs and other applicable legal requirements, and to manage supply chain(s);
•a continued acceptable safety and tolerability profile following any commercial approval of sofpironium bromide;
•ability to obtain favorable labeling for sofpironium bromide through regulators that allows for successful commercialization, given the drug may be marketed only to the extent approved by these regulatory authorities (unlike with most other industries);
•acceptance by physicians, insurers and payors, and patients of the quality, benefits, safety, and efficacy of sofpironium bromide, if and where approved, including relative to alternative and competing treatments and the next best standard of care;
•existence of a pricing, insurance coverage and reimbursement environment conducive to the success of sofpironium bromide; and
•level of competition, including from other products earlier to market and from generic competition upon expiration of patent protection.
Although Botanix has reported it plans to submit an NDA for sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, to the FDA in the third quarter of 2022, there can be no assurance that it will receive the necessary approvals. If approval is denied or delayed, we may not receive any of the payments from Botanix provided for in the Asset Purchase Agreement. Even if regulatory approvals are obtained, sofpironium bromide gel, 15%, may not be successfully commercialized and may not generate sufficient revenue for us to receive any such payments.
In addition, certain of the payments that would be due to us from Botanix would be triggered by milestones that do not involve receipt of funds by Botanix, and therefore our receipt of such payments would depend on Botanix’s sufficiency of funds to pay us.
While we assigned the Kaken Agreement to Botanix in May 2022, we remain eligible to receive a portion of future regulatory and sales milestone payments and tiered earnout payments based on a percentage of net sales of ECCLOCK pursuant to the terms of the Asset Purchase Agreement. Kaken has final decision-making authority for the overall regulatory, development, and commercialization strategy for sofpironium bromide, market access activities, pricing and reimbursement activities, promotion, distribution, packaging, sales, and safety and pharmacovigilance in Japan and certain other Asian countries. As a result, Kaken substantially controls commercialization of ECCLOCK in Japan and may make decisions regarding commercialization that may reduce or eliminate the royalties and other payments due to us. We will not receive additional milestone or other payments from Botanix related to Kaken’s sales if Kaken does not continue to be successful in its development, regulatory, or commercial activities, if the approval is withdrawn for any reason, or if Kaken is unable to maintain an adequate price for ECCLOCK in Japan.
We currently have limited marketing capabilities and no sales organization. If we are unable to generate adequate financing, establish sales and marketing capabilities on our own or through third parties, or are delayed in establishing these capabilities, we will be unable to successfully commercialize our product candidates, if approved, or generate meaningful product revenue.
We currently have limited marketing capabilities and no sales organization and limited cash runway. To commercialize our product candidates, if approved, we must continue to obtain additional financing, build our marketing, sales, distribution, managerial, and other non-technical capabilities or make arrangements with third parties to perform these services, and we may not be successful in doing any of these. As a company, we have no prior experience in the commercial launch, marketing, sale, and distribution of pharmaceutical products, and there are significant risks involved in building and managing a sales organization, including our ability to fund costs and expenses of a sales organization and its activities, hire, retain, and incentivize qualified individuals, generate sufficient sales leads, or contract for a sales force and in either case, provide adequate training to sales and marketing personnel, and effectively manage a geographically dispersed sales and marketing team so they operate in an effective and compliant way. Any failure or delay in the development of our internal (or external contracted-for) sales, marketing, distribution, and pricing/reimbursement/access capabilities would impact
adversely the commercialization of these products. In addition, we may need more than one approved and marketed product to sustain employing an internal sales force.
We may choose to collaborate with third parties in various countries, including the U.S., that have direct sales forces, commercial and regulatory capacities, and established distribution systems, either to augment our own sales force and distribution systems or in lieu of our own sales force and distribution systems. We may not have sufficient financial resources to enter into and pay for such arrangements, and/or we may not be able to find adequate business partners. If we are unable to enter into such arrangements on acceptable terms or at all, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our current or future product candidates. The inability to commercialize successfully our product candidates, either on our own or through collaborations or partnerships with one or more third parties, would harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Our business and operations would suffer in the event of system failures, illegal stock trading or manipulation by external parties, cyber-attacks, or a deficiency in or exploitation of our cyber-security.
We rely on cloud-based software to provide the functionality necessary to operate our company, utilizing what is known as “software as a service” (“SaaS”). SaaS allows users like us to connect to and use cloud-based applications over the Internet, such as email, calendaring, and office tools. SaaS provides us with a complete software solution that we purchase on a subscription basis from a cloud service provider. Despite our efforts to protect confidential and sensitive information from unauthorized disclosure across all our platforms, and similar efforts by our cloud service provider(s) and our other third-party contractors, consultants, and vendors, whether information technology (“IT”) providers or otherwise, including but not limited to our CROs, law firms, accountants, and even the government regulators who we rely on to advance our business, this information, and the systems used to store and transmit it, are vulnerable to damage from computer viruses, unauthorized access, computer hacking or breaches, natural disasters, epidemics and pandemics, terrorism, war, labor unrest, and telecommunication and electrical failures. The risk of a security breach or disruption, particularly through cyber-attacks or cyber-intrusion, or other illegal acts, including by computer hackers, foreign governments, and cyber-terrorists, has generally increased as the number, intensity, and sophistication of attempted attacks and intrusions from around the world have increased. Other emerging threats we face include: phishing, account takeover attacks, data breach or theft (no matter where the data are stored), loss of control, especially in SaaS applications, over which users have access to what data and level of access, new malware, zero-day threats, and threats within our own organization. In addition, and probably exacerbated by the COVID-19 pandemic and increased remote working arrangements, malicious cyber actors may increase malware and ransom campaigns and phishing emails targeting teleworkers as well as company systems, preying on the uncertainties surrounding COVID-19 or other world trends and events, which exposes us to additional cybersecurity risks, or may try to illegally obtain inside information to manipulate our stock price. If such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, or substantial manipulation of our stock price, it could result in a material disruption of our development programs and our business operations. In addition, since we sponsor clinical trials, any breach that compromises patient data and identities, thereby causing a breach of privacy, could generate significant reputational damage and legal liabilities and costs to recover and repair, including affecting trust in us to recruit for future clinical trials. For example, the loss or theft of clinical trial data from completed, ongoing, or future clinical trials could result in delays in our regulatory approval efforts, stock manipulation, and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability or suffer from stock price volatility or decline, and the further development and commercialization of our products and product candidates could be delayed.
We may be adversely affected by natural disasters and other catastrophic events and by man-made problems such as war or terrorism or labor disruptions that could disrupt our business operations, and our business continuity and disaster recovery plans may not adequately protect us from a serious disaster.
Our corporate office is located in Boulder, Colorado, near a major flood and blizzard zone and in an area prone to wildfires. If a disaster, power outage, or other event occurred that prevented us from using all or a significant portion of our office, that damaged critical infrastructure, or that otherwise disrupted operations, it may be difficult or, in certain cases, impossible for us to continue our business for a period of time. Our contract manufacturers’ and suppliers’ facilities are located in multiple locations where other natural disasters or similar events, such as tornadoes, earthquakes, storms, fires, explosions or large-scale accidents or power outages, could severely disrupt our operations, could expose us to liability and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects. All of the aforementioned risks may be further increased if we do not implement an adequate disaster recovery plan or our partners’ or manufacturers’ disaster recovery plans prove to be inadequate.
Risks Related to Our Liquidity, Financial Matters, and Our Common Stock
We will need to raise substantial additional financing in the future to fund our operations, which may not be available to us on favorable terms or at all.
We will require substantial additional funds to develop and, if successful, commercialize our product candidates. Our future capital requirements will depend upon a number of factors, including but not limited to: the number and timing of future product candidates in the pipeline; progress with and results from preclinical testing and clinical trials; the ability to obtain sufficient drug supplies to complete preclinical and clinical trials; the costs involved in preparing, filing, acquiring, prosecuting, maintaining and enforcing patent and other intellectual property claims; compliance with our material contracts including the licensing agreements for our autoimmune and inflammatory portfolio; the time and costs involved in obtaining regulatory approvals and favorable reimbursement or formulary acceptance for such product candidates; and overall stock market conditions, global business trends, our stock price performance, and our ability to generate funding under these and other conditions.
Raising additional capital may be costly or difficult to obtain and could significantly dilute stockholders’ ownership interests or inhibit our ability to achieve our business objectives. If we raise additional funds through public or private equity offerings, the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our common stockholders. Further, to the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of common stock or securities convertible or exchangeable into common stock, our stockholders’ ownership interests in our company will be diluted. In addition, any debt financing may subject us to fixed payment obligations and covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures, or declaring dividends. If we raise additional capital through marketing and distribution arrangements or other collaborations, strategic alliances, or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish certain valuable intellectual property or other rights to our product candidates, technologies, future revenue streams or research programs or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us in one or more countries.
Our ability to raise additional funds is uncertain and is limited given our small market capitalization and current stock price. Due to the SEC’s “baby shelf rules,” which prohibit companies with a public float of less than $75 million from issuing securities under a shelf registration statement in excess of one-third of such company’s public float in a 12-month period, we are only able to issue a limited number of shares which aggregate to no more than one-third of our public float using our shelf registration statement at this time. Even if sufficient funding is available, there can be no assurance that it will be available on terms acceptable to us or our stockholders.
We are currently operating in a period of economic uncertainty and capital markets disruption, which has been significantly impacted by geopolitical instability due in part to the ongoing military conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be materially adversely affected by the negative impact on the global economy and capital markets resulting from the conflict in Ukraine or other geopolitical tensions.
U.S. and global markets are experiencing volatility and disruption following the escalation of geopolitical tensions and the military conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Although the length and impact of the ongoing military conflict is highly unpredictable, the conflict in Ukraine has led to market disruptions, including significant volatility in commodity prices, credit and capital markets, as well as supply chain disruptions.
Additionally, various of Russia’s actions have led to sanctions and other penalties being levied by the U.S., the European Union, and other countries, as well as other public and private actors and companies, against Russia and certain other geographic areas, including agreement to remove certain Russian financial institutions from the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication payment system and restrictions on imports of Russian oil, liquified natural gas, and coal. Additional potential sanctions and penalties have also been proposed and/or threatened. Russian military actions and the resulting sanctions could further adversely affect the global economy and financial markets and lead to instability and lack of liquidity in capital markets, potentially making it more difficult for us to obtain additional funds.
Any of the above-mentioned factors could affect our business, prospects, financial condition, and operating results. The extent and duration of the military action, sanctions, and resulting market disruptions are impossible to predict, but could be substantial. Any such disruptions may also magnify the impact of other risks described in this Quarterly Report.
Our operating results and liquidity needs could be affected negatively by global market fluctuations and economic downturns.
Our operating results and liquidity could be affected negatively by global economic conditions generally, both in the U.S. and elsewhere around the world, including but not limited to that related to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, the Russian invasion of Ukraine and related sanctions and global IT threats. The market for discretionary pharmaceutical products, medical devices, and procedures may be particularly vulnerable to unfavorable economic or other conditions. Domestic and international equity and debt markets are experiencing and may in the future experience heightened volatility and turmoil based on domestic and international economic conditions and concerns. In the event these economic conditions and concerns continue or worsen and the markets remain volatile, or an economic recession, including as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russian invasion of Ukraine and related sanctions or other stimulus, our operating results and liquidity could be affected adversely by those factors in many ways, making it more difficult for us to raise funds, and our stock price may decline.
Our stock price and volume of shares traded have been and may continue to be highly volatile, and our common stock may continue to be illiquid.
The market price of our common stock has been subject to significant fluctuations. Market prices for securities of biotechnology and other life sciences companies historically have been particularly volatile and subject even to large daily price swings. In addition, there has been limited liquidity in the trading market for our securities, which may adversely affect stockholders. Some of the factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to continue to fluctuate include, but are not limited to:
•our need for additional potential financings to raise funds to further develop and commercialize our pipeline assets, which could result in significant additional share dilution;
•material developments in, or the conclusion of, any litigation to enforce or defend any intellectual property rights or defend against the intellectual property rights of others;
•our ability to satisfy all listing requirements of The Nasdaq Capital Market and the impact that may result from any future deficiencies,
•the entry into, or termination of, or breach by us or our partners of material agreements, including key commercial partner or licensing agreements;
•our ability to obtain timely regulatory approvals for our product candidates, and delays or failures to obtain such approvals;
•issues in manufacturing or the supply chain for our product candidates;
•the results of any clinical trials of our pipeline assets;
•failure of our product candidates, if approved, to achieve commercial success;
•announcements of any dilutive equity financings;
•announcements by commercial partners or competitors of new commercial products, clinical progress or the lack thereof, significant contracts, commercial relationships, or capital commitments;
•the introduction of technological innovations or new therapies or formulations that compete with our pipeline assets;
•lack of commercial success of competitive products or products treating the same or similar indications;
•failure to elicit meaningful stock analyst coverage and downgrades of our stock by analysts, or to obtain more institutional shareholders; and
•the loss of key employees and/or inability to recruit the necessary talent for new positions or to replace exiting employees.
Moreover, the stock markets in general have experienced substantial volatility in our industry, especially for microcap biotechnology companies, and such volatility has often been unrelated to the operating performance of individual companies or a certain industry segment, such as the ongoing reaction of global markets to the COVID-19 pandemic, the Russian invasion of Ukraine and related sanctions and other economic disruptions or concerns, including inflation. These broad market fluctuations may also adversely affect the trading price of our common stock.
In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities, shareholders have often instituted class action securities litigation against those companies. Such litigation, if instituted, could result in substantial costs and diversion of management attention and resources, which could significantly harm our profitability and reputation and could expose us to liability or impact negatively our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Our operating results may fluctuate significantly, which makes our future operating results difficult to predict and could cause our operating results to fall below expectations.
Our operations to date have been limited primarily to business planning, raising capital, developing and entering into strategic partnerships for our pipeline assets, identifying and in-licensing product candidates, entering into sale arrangements that involve our rights to assets and related intellectual property, conducting clinical trials, and other research and development activities. Consequently, any predictions about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we had a longer operating history or approved products on the market. Our revenue and profitability will depend on development funding for our product portfolio, the receipt of sales milestones and earnout payments under the Asset Purchase Agreement, our ability to satisfy the
development and regulatory milestones under applicable in-license agreements, as well as our ability to do the same with regard to any potential future collaboration and license agreements, overall sales of any products, if approved, and our ability to maintain all of our product licenses. Any upfront, milestone, or earnout payments either owed by or to us may vary significantly from product to product, period to period, and country to country, and any such variance could cause a significant fluctuation in our operating results from one period to the next. In addition, we measure compensation cost for stock-based awards made to employees at the grant date of the award, based on the fair value of the award, and recognize the cost as an expense over the employee’s requisite service period. As the variables that we use as a basis for valuing these awards change over time, including our underlying stock price and stock price volatility, the magnitude of the expense that we must recognize may vary significantly. Furthermore, our operating results may fluctuate due to a variety of other factors, many of which are outside of our control and may be difficult to predict.
We are a “smaller reporting company” and the reduced disclosure and governance requirements applicable to smaller reporting companies may make our common stock less attractive to some investors.
We qualify as a “smaller reporting company” under Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. As a smaller reporting company, we are entitled to rely on certain exemptions and reduced disclosure requirements, such as simplified executive compensation disclosures and reduced financial statement disclosure requirements, in our SEC filings. These exemptions and decreased disclosures in our SEC filings due to our status as a smaller reporting company may make it harder for investors to analyze our results of operations and financial prospects. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our common stock price may be more volatile.
If the holders of our company’s stock options and warrants exercise their rights to purchase our common stock, the ownership of our stockholders will be diluted.
If the holders of our outstanding stock options and warrants exercise their rights to acquire our common stock and service conditions related to restricted stock units are met, the percentage ownership of our stockholders existing prior to the exercise of such rights will be diluted. As of June 30, 2022, we had outstanding warrants to purchase (i) one share of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.07 per share; (ii) 490,683 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $10.36 per share; (iii) 9,005 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $33.31 per share; (iv) 1,556,420 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $1.16 per share; (v) 17,482,500 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $1.25 per share; and (vi) 8,405,935 shares of our common stock at an exercise price of $0.72 per share. As of June 30, 2022, we also had 10,449,546 options issued and outstanding to purchase our common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $2.07 per share.
We are significantly limited in our ability to make sales under the Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park, which could prevent us from accessing the capital we need to continue our operations and have an adverse effect on our business.
On February 17, 2020, we entered into the Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park pursuant to which Lincoln Park agreed to purchase from us up to an aggregate of $28.0 million of our common stock (subject to certain limitations) from time to time over the 36-month period commencing on August 14, 2020. As of June 30, 2022, approximately $26.9 million of shares of common stock were remaining, but had not yet been sold, under the Purchase Agreement. However, only 57,751 of such shares (less than $175,000 of shares assuming a sale date of August 11, 2022) have been registered by us under the Securities Act.
As a result, our ability to raise capital pursuant to the Purchase Agreement will be materially limited unless we register a significant number of additional shares under the Securities Act. Even if we are ultimately able to sell all shares under the Purchase Agreement, we will still need additional capital to fully implement our business, operating, and development plans.
Our ability to maintain compliance with Nasdaq continued listing requirements, including if we are unable to maintain the closing bid price of our common stock, could result in the delisting of our common stock.
Our common stock is currently listed on The Nasdaq Capital Market. In order to maintain this listing, we must satisfy minimum financial and other requirements. On June 17, 2021, we received a notice from the Listing Qualifications Department of Nasdaq informing us that because the closing bid price for our common stock listed on Nasdaq was below $1.00 per share for 30 consecutive business days, we were not in compliance with the minimum closing bid price requirement for continued listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market under Nasdaq Marketplace Rule 5550(a)(2) (the “Rule”). We initially had a period of 180 calendar days, or until December 13, 2021, to regain compliance with the Rule. In December 2021, Nasdaq provided notice that granted us an additional 180 calendar days, or until June 13, 2022, to regain compliance with the Rule.
On June 14, 2022, Nasdaq notified us that we did not regain compliance with the Rule as of June 13, 2022, and therefore our common stock would be delisted from The Nasdaq Capital Market, unless we appealed the delisting determination by timely requesting a hearing before the Nasdaq Hearings Panel. We timely requested the hearing, which request stayed any further delisting action, and a hearing was scheduled. On July 5, 2022, we effected the 1-for-45 reverse stock split and subsequently the closing price of our common stock was in excess of $1.00 for 10 consecutive trading days. On July 19, 2022, we received formal notice from Nasdaq stating that we regained compliance with the Rule and, accordingly, the previously-scheduled hearing regarding the delisting action was canceled and our common stock will continue to be listed and traded on Nasdaq.
However, there can be no assurance that our stock price will continue to meet the minimum bid price requirement or other requirements for continued listing on Nasdaq. If our common stock is delisted from Nasdaq and we are unable to list our common stock on another national securities exchange, we expect our common stock would be quoted on an over-the-counter market. If this were to occur, we and our stockholders could face significant material adverse consequences, including limited availability of market quotations for our common stock; substantially decreased trading in our common stock; decreased market liquidity of our common stock as a result of the loss of market efficiencies associated with Nasdaq and the loss of federal preemption of state securities laws; an adverse effect on our ability to issue additional securities or obtain additional financing in the future on acceptable terms, if at all; potential loss of confidence by investors, suppliers, partners, and employees and fewer business development opportunities; and limited news and analyst coverage. Additionally, the market price of our common stock may decline further, and shareholders may lose some or all of their investment.
Even if we are not delisted, the perception among investors that we are at a heightened risk of delisting could negatively affect the market price and trading volume of our common stock, or our ability to raise capital.
The reverse stock split of our common stock may have negative consequences, including making our stock less attractive to certain investors, decreasing liquidity and resulting in higher transaction costs.
Although the reverse stock split increased the market price of our common stock for a period of time sufficient to regain compliance with the minimum bid price requirement for continued listing on Nasdaq, some investors may view a reverse stock split negatively, including resulting in a stock price that is still not sufficient to attract investors who do not trade in lower priced stocks. In addition, declines in the trading price of our common stock following the reverse stock split result in percentage declines as an absolute number and as a percentage of our overall market capitalization greater than would occur in the absence of the reverse stock split.
Further, the liquidity of our common stock may be negatively impacted by the reverse stock split, given the reduced number of shares outstanding after the reverse stock split. The reverse stock split also increased the number of our stockholders who own “odd lots” of fewer than 100 shares of common stock. Brokerage commissions and other costs of transactions in odd lots are generally higher than the costs of transactions of more than 100 shares of common stock.
In addition, although the reverse stock split did not have any immediate dilutive effect on our stockholders, the number of shares of our common stock authorized for issuance was not proportionately decreased, and therefore the reverse stock split had the effect of reducing the proportion of shares owned by our stockholders relative to the number of shares authorized for issuance, giving our board of directors an effective increase in the relative number of authorized shares available for issuance, in its discretion. The issuance of additional shares of our common stock subsequent to the reverse stock split may result in dilution to the ownership interest of our existing stockholders that is greater than would occur had the reverse stock split not been effected.
We do not anticipate paying any dividends in the foreseeable future.
Our current expectation is that we will retain any future earnings to fund the development and growth of our business. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our shares will be your sole source of gain, if any, for the foreseeable future.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and other tax assets to offset future taxable income may be subject to certain limitations.
As of December 31, 2021, we had approximately $455.9 million of federal and $429.0 million of state net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards available to offset future taxable income, of which $173.5 million will carryforward indefinitely and the remainder expiring in varying amounts beginning in 2022 for federal and state purposes if unused. Utilization of these NOLs depends on many factors, including our future income, which cannot be assured. Under the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Acts (“Tax Act”), U.S. federal NOLs incurred in 2018 and later years may be carried forward indefinitely, but our ability to utilize such U.S. federal NOLs to offset taxable income is limited to 80% of the current-year taxable income. In addition, under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 and corresponding provisions of state law, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change” (which is generally defined as a greater than 50 percentage points change (by value) in its equity ownership over a rolling three-year period), the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change NOL carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change income or taxes may be limited. We have not determined whether we have experienced Section 382 ownership changes in the past and if a portion of our NOLs is therefore subject to an annual limitation under Section 382. Therefore, we cannot provide any assurance that a change in ownership within the meaning of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 and corresponding provisions of state law has not occurred in the past, and there is a risk that changes in ownership could have occurred. We may experience ownership changes as a result of subsequent changes in our stock ownership, as a result of offerings of our stock or subsequent shifts in our stock ownership, some of which may be outside of our control. In that case, the ability to use NOL carryforwards to offset future taxable income will be limited following any such ownership change and could be eliminated. If eliminated, the related asset would be removed from the deferred tax asset schedule with a corresponding reduction in the valuation allowance on our financial statements.
Risks Related to Legal, Regulatory, and Compliance Matters
We and our partners may never obtain regulatory approval to commercialize any other product candidates, and any products approved for sale will be subject to continued regulatory review and compliance obligations and there could be further restrictions on post-approval activities, including commercialization efforts. In obtaining regulatory approval, the approved product label (aka package insert) will determine the extent of allowed promotional activities, and this label could be restrictive or prohibitory with regard to subject matter that may be necessary to maximize the commercial success of the products that are approved.
The research, testing, manufacturing, safety surveillance, efficacy, quality assurance and control, recordkeeping, labeling, packaging, storage, approval, sale, marketing, distribution, import, export, and reporting of safety and other post-market information related to our investigational drug products are subject to extensive regulation by
the FDA and other regulatory authorities in the U.S. and foreign countries, and such regulations differ from country to country and frequently are revised.
Even after we or our partners achieve regulatory approval for a product candidate, if any, we or our partners will be subject to continued regulatory review and compliance obligations, including on how the product is commercialized. For example, with respect to our product candidates for the U.S., the FDA may impose significant restrictions on the approved indicated use(s) for which the product may be marketed or on the conditions of approval. A product candidate’s approval may contain requirements for potentially costly post-approval studies and surveillance, including Phase 4 clinical trials, to monitor the safety and efficacy of the product or include in the approved label restrictions on the product and how it may be used or sold. Approved products also will be subject to ongoing FDA obligations and continued regulatory review with respect to, among other things, the manufacturing, processing, labeling, packaging, distribution, pharmacovigilance and adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion, and recordkeeping for our product candidates. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration, continued compliance with cGMP requirements and with the FDA’s GCP requirements and GLP requirements, which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the FDA for all of our product candidates in clinical and preclinical development, and for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval, as well as continued compliance with the FDA’s laws governing commercialization of the approved product, including but not limited to the FDA’s Office of Prescription Drug Promotion’s regulation of promotional activities and direct-to-consumer advertising, fraud and abuse, antikickback, product sampling, debarment, scientific speaker engagements and activities, formulary interactions as well as interactions with healthcare practitioners, including various conflict-of-interest reporting requirements for any healthcare practitioners we may use as consultants, and laws relating to the pricing of drug products, including federal “best price” regulations that if not met can prohibit us from participating in federal reimbursement programs like Medicare or Medicaid. To the extent that a product candidate is approved for sale in other countries, it may be subject to similar or more onerous (e.g., prohibition on direct-to-consumer advertising and price controls that do not exist in the U.S.) restrictions and requirements imposed by laws and government regulators, and even private institutions, in those countries.
In addition, manufacturers of drug and biologic products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMP regulations. If we, our partners, or a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the manufacturing, processing, distribution, or storage facility where, or processes by which, the product is made, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product, us or our partners, including requesting that we or they initiate a product recall, or requiring notice to physicians or the public, withdrawal of the product from the market, or suspension of manufacturing.
If we, our partners, our product candidates, or the manufacturing facilities for our product candidates fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, a regulatory agency may:
•impose restrictions on the sale, marketing, advertising, or manufacturing of the product, or amend, suspend, or withdraw product approvals, or revoke necessary licenses;
•mandate modifications to or prohibit promotional and other product-specific materials or require us or our partners to provide corrective information to healthcare practitioners and other customers and/or patients, or in our or their advertising and promotion;
•require us or our partners to enter into a consent decree, which can include imposition of various fines, reimbursements for inspection costs, required due dates for specific actions, penalties for noncompliance and, in extreme cases, require an independent compliance monitor to oversee our activities;
•issue warning letters, bring enforcement actions, initiate surprise inspections, issue show cause notices or untitled letters describing alleged violations, which may be publicly available;
•commence criminal investigations and prosecutions;
•debar certain healthcare professionals;
•exclude us or our partners from participating in or being eligible for government reimbursement and formulary inclusion;
•initiate audits, inspections, accounting and civil investigations, or litigation;
•impose injunctions, suspensions, or revocations of necessary approvals or other licenses;
•impose other civil or criminal penalties;
•suspend or cancel any ongoing clinical trials;
•place restrictions on the kind of promotional activities that can be done;
•delay or refuse to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications filed by us or our partners;
•refuse to permit drugs or precursor chemicals to be imported or exported to or from the U.S.;
•suspend or impose restrictions on operations, including costly new manufacturing requirements;
•change or restrict product labeling; or
•seize or detain products or require us or our partners to initiate a product recall.
The regulations, policies, or guidance of the FDA and other applicable government agencies may change quickly, and new or additional statutes or government laws or regulations may be enacted, including at federal, state, and local levels, or case law may issue, which can differ by geography and could prevent or delay regulatory approval of product candidates or further restrict or regulate post-approval activities, including commercialization efforts. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature, or extent of adverse government regulations that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, or judicial outcomes based on litigation, either in the U.S. or abroad. If we or our partners are not able to achieve and maintain regulatory or other legal compliance, we or they may not be permitted to commercialize product candidates, which would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue and achieve or maintain profitability.
We have sponsored or supported and in the future expect to sponsor or support clinical trials for our product candidates outside the U.S., and the FDA and applicable foreign regulatory authorities may not accept data from such trials; in addition, we may not be allowed alone or with local country business partners to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates without first conducting clinical trials in each of these other countries.
We have sponsored or supported and expect to continue to sponsor or support one or more of our clinical trials outside of the U.S., including our currently ongoing Phase 1 clinical trial for BBI-02 in Canada. Although the FDA or applicable foreign regulatory authorities may accept data from clinical trials conducted outside the U.S. or the applicable jurisdiction, acceptance of such study data by the FDA or applicable foreign regulatory authorities may be subject to certain conditions or exclusions. Where data from foreign clinical trials are
intended to serve as the basis for marketing approval in the U.S., the FDA will not approve the application on the basis of foreign data alone unless such data are applicable to the U.S. population and U.S. medical practice; the studies were performed by clinical investigators of recognized competence; and the data are considered valid without the need for an on-site inspection by the FDA or, if the FDA considers such an inspection to be necessary, the FDA is able to validate the data through an on-site inspection or other appropriate means. Many foreign regulatory bodies have similar requirements. In addition, such foreign studies would be subject to the applicable local laws of the foreign jurisdictions where the studies are conducted. There can be no assurance the FDA or applicable foreign regulatory authorities will accept data from trials conducted outside of the U.S. or the applicable home country. If the FDA or applicable foreign regulatory authority does not accept such data, it would likely result in the need for additional clinical trials, which would be costly and time-consuming and delay aspects of our business plan.
We may face product liability exposure, and if successful claims are brought against us, we may incur substantial liability if our insurance coverage for those claims is inadequate.
We face an inherent risk of product liability or similar causes of action as a result of the clinical testing (and use) of our product candidates and will face an even greater risk if we commercialize any products. This risk exists even if a product is approved for commercial sale by the FDA and is manufactured in facilities licensed and regulated by the FDA or an applicable foreign regulatory authority and notwithstanding that we comply with applicable laws on promotional activity. Our products and product candidates are designed to affect important bodily functions and processes. Any side effects, manufacturing defects, misuse, or abuse associated with our product candidates could result in actual or perceived injury to a patient that may or may not be reversible or potentially even cause death. We cannot offer any assurance that we will not face product liability or other similar suits in the future or that we will be successful in defending them, nor can we assure that our insurance coverage will be sufficient to cover our liability under any such cases.
In addition, a liability claim may be brought against us even if our product candidates merely appear to have caused an injury. Product liability claims may be brought against us by consumers, healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, or others selling or otherwise coming into contact with our product candidates, among others, and under some circumstances even government agencies. If we cannot successfully defend against product liability or similar claims, we will incur substantial liabilities, reputational harm, and possibly injunctions and punitive actions. In addition, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, product liability claims may result in:
•withdrawal or delay of recruitment or decreased enrollment rates of clinical trial participants;
•termination or increased government regulation of clinical trial sites or entire trial programs;
•the inability to commercialize, or restrictions on commercializing, our product candidates;
•decreased demand for our product candidates;
•impairment of our business reputation;
•product recall or withdrawal from the market or labeling, marketing, or promotional restrictions;
•substantial costs of any related litigation or similar disputes;
•distraction of management’s attention and other resources from our primary business;
•significant delay in product launch;
•debarment of our clinical trial investigators or other related healthcare practitioners working with our company;
•substantial monetary awards to patients or other claimants against us that may not be covered by insurance;
•withdrawal of reimbursement or formulary inclusion; or
•loss of revenue.
We have obtained product liability insurance coverage for our clinical trials. Large judgments have been awarded in class action or individual lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects. Our insurance coverage may not be sufficient to cover all of our product liability-related expenses or losses and may not cover us for any expenses or losses we may suffer. Moreover, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive, restrictive, and narrow, and, in the future, we may not be able to maintain adequate insurance coverage at a reasonable cost, or through self-insurance, in sufficient amounts or upon adequate terms to protect us against losses due to product liability or other similar legal actions. We will need to increase our product liability coverage if any of our product candidates receive regulatory approval, which will be costly, and we may be unable to obtain this increased product liability insurance on commercially reasonable terms or at all and for all geographies in which we wish to launch. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us could, if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, decrease our cash, expose us to liability and harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
We may be subject to risks related to pre-approval promotion or off-label use, or unauthorized direct-to-consumer advertising, of our product candidates.
In the U.S., the FDA strictly regulates the advertising and promotion of drug products, and drug products may only be marketed or promoted for their FDA-approved uses, consistent with the product’s approved labeling and to appropriate patient populations. Advertising and promotion of any product candidate that obtains approval in the U.S. will be heavily scrutinized by the FDA, the Department of Justice, the Office of Inspector General of the Department of Health and Human Services (“HHS”), state attorneys general, members of Congress, the public, and others. Violations, including promotion of our products for unapproved or off-label uses, or inappropriate direct-to-consumer advertising, are subject to enforcement letters, inquiries and investigations, and civil, criminal, and/or administrative sanctions by the FDA and other government agencies or tribunals and lawsuits by competitors, healthcare practitioners, consumers, investors, or other plaintiffs. Additionally, advertising and promotion of any product candidate that obtains approval outside of the U.S. will be heavily scrutinized by relevant foreign regulatory authorities.
Even if we or our partners obtain regulatory approval for product candidates, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require labeling changes or impose significant restrictions on a product’s indicated uses or marketing, or impose ongoing requirements for potentially costly post-approval studies or post-market surveillance.
In the U.S., engaging in impermissible promotion of our product candidates for off-label uses, or engaging in pre-approval promotion of an unapproved drug candidate, also can subject us to false claims litigation under federal and state statutes, which can lead to civil, criminal and/or administrative penalties and fines and agreements, such as a corporate integrity agreement, that materially restrict the manner in which we promote or distribute our product candidates. If we do not lawfully promote our products once they have received regulatory approval, we may become subject to such litigation and, if we are not successful in defending against such actions, those actions could expose us to liability and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects and even result in having an independent compliance monitor assigned to audit our ongoing operations at our cost for a lengthy period of time.
Healthcare reform measures, including price controls or restricted access, could hinder or prevent the commercial success of our product candidates in any country.
The enactment of any new healthcare initiatives or pharmaceutical industry regulations could have significant impacts on our ability to advance the development of our product candidates and eventually to commercialize them, if at all. Specifically, on September 9, 2021, the Biden White House released a Prescription Drug Pricing Plan (“Plan”) to reduce prescription drug prices and out-of-pocket costs for patients. This Plan highlights legislative policies that the White House supports to lower drug prices by allowing the Secretary of HHS to negotiate Medicare Part B (physician-administered) and Part D (outpatient) drug prices directly with pharmaceutical companies and make those prices available in the commercial market. However, to date, details are limited as to what these negotiations might look like. The Plan also pledges support for a redesign of the Medicare Part D program that would institute a lower cap on out-of-pocket spending to protect beneficiaries by shifting significantly more of the cost management burden onto payers and drug manufacturers after a Medicare beneficiary reaches his or her out-of-pocket spending limit. The Plan also aims to curb annual price increases of existing drugs covered by Medicare Parts B and D, imposing an inflationary rebate for those that exceed an unspecified inflation index (consumer or medical price inflation index). HHS also may pursue other administrative actions without Congress. While these proposals have not yet been enacted, we expect that additional state and federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in reduced demand for our product candidates if approved or additional pricing pressures.
There are also calls to severely curtail or ban all direct-to-consumer advertising of pharmaceuticals or restrict activities by pharmaceutical sales representatives to have access to prescribers, which would limit our ability to market our product candidates. With regard to marketing directly to consumers and patients, the U.S. is in a minority of jurisdictions that even allow this kind of advertising, and its removal could limit the potential reach of a marketing campaign.
We are and may be subject to strict healthcare laws, regulation, and enforcement, and our failure to comply with those laws could expose us to liability or adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Certain federal and state healthcare laws and regulations pertaining to fraud and abuse and patients’ rights and privacy are and will be applicable to our business. We are subject to regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we or our partners conduct business. The healthcare laws and regulations that may affect our ability to operate include: the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, as amended; Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations Part 202 (21 CFR Part 202); the 21st Century Cures Act, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute; federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws; the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act; the Prescription Drug Marketing Act (for sampling of drug product); the federal Best Price Act and Medicaid drug rebate program; the federal physician sunshine reporting requirements under the Affordable Care Act and state disclosure laws; the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act as it applies to activities both inside and outside of the U.S.; the federal Right-to-Try legislation; and state law equivalents of many of the above federal laws.
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and safe harbors available, it is possible that some of our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. In addition, healthcare reform legislation has strengthened these laws. For example, the Affordable Care Act, among other things, amended the intent requirement of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and certain criminal healthcare fraud statutes. A person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it. In addition, the Affordable Care Act provides that the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the federal civil False Claims Act.
Achieving and sustaining compliance with these laws may prove costly. In addition, any action against us for violation of these laws, even if we successfully defend against it, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert our management’s attention from the operation of our business and result in reputational damage. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other governmental laws or regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including administrative, civil, and criminal penalties, damages, including punitive damages, fines, disgorgement, the exclusion from participation in federal and state healthcare programs, individual imprisonment or corporate criminal liability, or the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, and injunctions, any of which could expose us to liability and could adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
We may seek orphan drug exclusivity for some of our product candidates, and we may be unsuccessful.
Regulatory authorities in some jurisdictions, including the United States and Europe, may designate drugs for relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a product as an orphan drug if it is a drug intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally defined as a disease with a patient population of fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States.
Generally, if a product with an orphan drug designation subsequently receives the first marketing approval for the indication for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to a period of marketing exclusivity, which precludes the European Medicines Agency (the “EMA”) or the FDA from approving another marketing application for the same drug for the same indication during the period of exclusivity. The applicable period is seven years in the United States and ten years in Europe. The European exclusivity period can be reduced to six years if a drug no longer meets the criteria for orphan drug designation or if the drug is sufficiently profitable so that market exclusivity is no longer justified. Orphan drug exclusivity may be lost if the FDA or EMA determines that the request for designation was materially defective, or if the manufacturer is unable to assure sufficient quantity of the drug to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition.
Even if we obtain orphan drug exclusivity for a product candidate, that exclusivity may not effectively protect the product candidate from competition because different drugs can be approved for the same condition. Even after an orphan drug is approved, the FDA can subsequently approve a different drug for the same condition if the FDA concludes that the later drug is clinically superior in that it is shown to be safer, more effective or makes a major contribution to patient care.
Our employees, independent contractors, principal investigators, other clinical trial staff, consultants, vendors, CROs, and any partners with which we may collaborate may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements.
We are exposed to the risk that our employees, officers, directors, independent contractors, principal investigators, other clinical trial staff, consultants, advisors, vendors, CROs, and any partners with which we may collaborate may engage in fraudulent or other illegal or unethical activity. Misconduct by these persons could include intentional, reckless, gross or negligent misconduct or unauthorized activity that violates: laws or regulations, including those laws requiring the reporting of true, complete, and accurate information to the FDA or foreign regulatory authorities; product sampling; manufacturing standards; federal, state and foreign healthcare fraud and abuse laws and data privacy; anticorruption laws, anti-kickback and Medicare/Medicaid rules, debarment laws, promotional laws, securities laws, and/or laws that require the true, complete and accurate reporting of financial information or data, books, and records. If any such or similar actions are instituted against us and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of civil, criminal and administrative and punitive penalties, damages, monetary fines, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid, and other federal or state healthcare programs, debarments, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, injunctions, and curtailment or cessation of our operations, any of which could expose us to liability and adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
We incur costs and demands upon management as a result of complying with the laws and regulations affecting public companies.
We incur significant legal, accounting, and other expenses to operate as a public company, including costs associated with public company reporting and other SEC requirements. We also incur costs associated with corporate governance requirements, including requirements under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules implemented by the SEC and Nasdaq. These rules and regulations have, and are expected to continue to, increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. These rules and regulations may also make it expensive for us to operate our business.
Risks Related to Strategic Matters
We intend to continue to in-license and acquire product candidates and may engage in other strategic transactions, which could impact our liquidity, increase our expenses, and present significant distractions to our management.
One of our ongoing strategies is to in-license and acquire additional product candidates, and we may engage in other strategic transactions. Additional potential transactions that we may consider include a variety of different business arrangements, including mergers and acquisitions, spin-offs, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, co-marketing, co-promotion, distributorships, development and co-development, royalty monetization, restructurings, divestitures, business combinations, contract sales forces, out-licensing or divesture of existing products, and investments on a global basis. Any such transaction(s) may require us to incur non-recurring or other charges, may increase our near- and long-term expenditures, and may cause us to grow and expand rapidly, putting pressure on current resources and capabilities, and may pose significant integration challenges or disrupt our management or business, which could adversely affect our operations and financial results. Further, any such transaction(s) may require us to obtain additional financing, which may not be available to us on favorable terms or at all. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that we will undertake or successfully complete future transactions of the nature described above, and any transaction that we do complete could expose us to liability, delays, and implementation obstacles that could harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects. We have no current commitment or obligation to enter into any transaction described above other than ones to which we are already committed.
We may choose not to continue developing or commercializing any of our product candidates at any time during development or after approval, or we may sell and assign our rights, which would reduce or eliminate our potential return on investment for those product candidates.
At any time, we may decide to discontinue the development or commercialization of any of our early-stage or licensed rights to product candidates, or sell and assign our rights, for a variety of reasons, including the appearance of new technologies that make our product obsolete or significantly impact the ability to commercialize the affected product successfully, competition from a competing product including entry of generics, supply chain considerations, intellectual property right impacts, ability to price or changes in or failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, inability or difficulty to generate financing to commercialize a product, market reaction to the market potential for any product asset, or constraints on obtaining additional financing and capital. If we terminate, exit, or assign a program in which we have invested significant resources, we either likely will not receive any return, or only a partial return, on our investment, and we may have missed an opportunity to have allocated those resources to potentially more productive uses.
Our failure to in-license, acquire, develop, and market successfully additional product candidates or approved products would impair our ability to grow our business.
We have, and intend to continue to, in-license, acquire, develop, and market additional products and product candidates. Because our internal research and development capabilities are limited, we may be dependent on
pharmaceutical or other companies, investment groups or funds, academic or government scientists, and other researchers to sell or license products or technology to us. The success of this strategy depends partly on our ability to identify and select promising pharmaceutical product candidates and products, negotiate licensing or acquisition agreements with their current owners, and finance these arrangements.
The process of proposing, negotiating, and implementing a license or acquisition of a product candidate or approved product is lengthy and complex. Other companies, including some with substantially greater financial, marketing, sales, legal and other resources, may compete with us for the license or acquisition of product candidates and approved products. We have limited resources to identify and execute the acquisition or in-licensing of third-party products, businesses, and technologies and integrate them into our current infrastructure. Moreover, we may devote resources to potential acquisitions or licensing opportunities that are never completed, or we may fail to realize the anticipated benefits of such efforts. We may not be able to acquire the rights to additional product candidates on terms that we find acceptable or at all.
Further, any product candidate that we maintain rights to or acquire may require (or, in the case of the pipeline assets we licensed from Voronoi and Carna, do require) additional development efforts prior to commercial sale, including preclinical or clinical testing and approval by the FDA and applicable foreign regulatory authorities for the targeted use(s), or present with significant integration issues. All product candidates are prone to significant risks of failure typical of pharmaceutical product development, including the possibility that a product candidate will not be shown to be sufficiently safe and effective for approval by regulatory authorities. In addition, we cannot provide assurance that any approved products that we acquire will be manufactured or sold profitably, obtain reimbursement, be subject to patents and other intellectual property rights that provide any form of market or regulatory exclusivity, sustain historical levels of performance that made the acquisition initially attractive, or achieve/maintain market acceptance.
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
We expect to rely on our collaboration with third-party partners for the successful development and commercialization of our product candidates.
We expect to rely upon the efforts of third-party partners for the successful development and commercialization of our current and future product candidates. The clinical, regulatory, and commercial success of our product candidates may depend upon maintaining successful relationships with third-party partners which are subject to a number of significant risks, including the following:
•our partners’ ability to execute their responsibilities in a timely, cost-efficient, and compliant manner and to maintain their supply chain systems and safeguard their IT operations and their and our data;
•reduced control over supply, delivery, and manufacturing schedules;
•price increases and product reliability;
•our ability to attract and retain the right partners;
•manufacturing deviations from internal or regulatory specifications;
•quality or integrity incidents;
•the failure of partners to perform their obligations for technical, market, legal, or other reasons;
•misappropriation of our current or future product candidates;
•ability of partners to comply with applicable laws or continue their own operations based on their unique situations; and
•other risks in potentially meeting our current and future product commercialization schedule or satisfying the requirements of our end-users.
We cannot assure that we will be able to establish or maintain third-party partner relationships to successfully develop and commercialize our product candidates.
We rely and expect to continue to rely on third-party contractors for supply, manufacture, and distribution of preclinical, clinical, and commercial supplies, and possibly sales and promotion, of any future product candidates.
We do not currently have, nor do we plan to acquire, the infrastructure or internal capability to supply, store, manufacture, or distribute preclinical, clinical, or commercial quantities of drug substances or products. Additionally, we have not entered into a long-term commercial supply agreement to provide us with such drug substances or products. As a result, our ability to develop our product candidates is dependent, and our ability to supply our products commercially will depend, in part, on our ability to obtain the APIs and other substances and materials used in our product candidates successfully from third parties and to have finished products manufactured by third parties in accordance with regulatory requirements and in sufficient quantities for preclinical and clinical testing and commercialization. If we fail to develop and maintain supply and other technical relationships with these third parties, or global conditions like the COVID-19 pandemic significantly and adversely impact such third parties, we may be unable to continue to develop or commercialize our products and product candidates.
We do not have direct control over whether our contract suppliers and manufacturers will maintain current pricing terms, be willing (or able) to continue supplying us with APIs and finished products, or maintain adequate capacity and capabilities to serve our needs, including quality control, quality assurance, and qualified personnel. We are dependent on our contract suppliers and manufacturers for day-to-day compliance with applicable laws and cGMPs for production of both APIs and finished products. If the safety or quality of any product or product candidate or component is compromised due to a failure to adhere to applicable laws or for other reasons, we may not be able to commercialize or obtain regulatory approval for the affected product or product candidate successfully, and we may be held liable for injuries sustained as a result.
In order to conduct larger or late-stage clinical trials for our product candidates and supply sufficient commercial quantities of the resulting drug product and its components, if that product candidate is approved for sale, our contract manufacturers and suppliers will need to produce our drug substances and product candidates in larger quantities, more cost-effectively and, in certain cases, at higher yields than they currently achieve. If our third-party contractors are unable to scale up the manufacture of any of our product candidates successfully in sufficient quality and quantity and at commercially reasonable prices, or are shut down or put on clinical hold by government regulators, and we are unable to find one or more replacement suppliers or manufacturers capable of production at a substantially equivalent cost in substantially equivalent volumes and quality, and we are unable to transfer the processes successfully on a timely basis, the development of that product candidate and regulatory approval or commercial launch for any resulting products may be delayed, or there may be a shortage in supply, either of which could significantly harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
We expect to continue to depend on third-party contract suppliers and manufacturers for the foreseeable future. Our supply and manufacturing agreements, if any, do not guarantee that a contract supplier or manufacturer will provide services adequate for our needs. In addition, inflation and/or global supply chain disruptions may have a negative impact on our third-party contract suppliers’ and manufacturers’ ability to acquire the materials necessary for our business, and we could incur higher costs for certain goods or services due to inflation or
increased freight costs. Additionally, any damage to, destruction of, or threats to our third-party manufacturers’ or suppliers’ facilities, equipment, or systems, even by force majeure or by criminal acts, may significantly impair our ability to have our products and product candidates manufactured on a timely basis. Our reliance on contract manufacturers and suppliers further exposes us to the possibility that they, or third parties with access to their facilities and systems, will have access to and may misappropriate our trade secrets, clinical trial and other research data, or other proprietary information. In addition, the manufacturing facilities of certain of our suppliers may be located outside of the U.S. This may give rise to difficulties in importing our products or product candidates or their components into the U.S. or other countries, or otherwise protecting these assets.
Manufacturing and supply of the APIs and other substances and materials used in our product candidates and finished drug products is a complex and technically challenging undertaking, and there is potential for failure at many points in the manufacturing, testing, quality control and assurance, and distribution supply chain, as well as the potential for latent defects after products have been manufactured and distributed.
Manufacturing and supply of APIs, other substances and materials, and finished drug products are technically challenging. Changes beyond our direct control can impact the quality, volume, price, and successful delivery of our products and product candidates and can impede, delay, limit, or prevent the successful development and commercialization of our products and product candidates. Mistakes and mishandling, and/or disruptions in the supply chain, are not uncommon despite reasonable best efforts and can affect successful production and supply. Some of these risks include but are not limited to:
•failure of our manufacturers to follow cGMP or other legal requirements or mishandling of or adulterating product while in production or in preparation for transit;
•inability of our contract suppliers and manufacturers to efficiently and cost-effectively increase and maintain high yields and batch quality, consistency, and stability;
•difficulty in establishing optimal drug delivery substances and techniques, production and storage methods, and packaging and shipment processes;
•challenges in designing effective drug delivery substances and techniques, especially in light of competitor options;
•transportation and import/export risk, particularly given the global nature of our supply chain;
•delays in analytical results or failure of analytical techniques that we depend on for quality control/assurance and release of a product;
•natural disasters, strikes and labor disputes, epidemics or pandemics, war and terrorism, financial distress, lack of raw material supply, issues with facilities and equipment, third-party criminal threats such as IT malware and/or ransom attempts caused by holding systems hostage, or other forms of disruption to business operations of our contract manufacturers and suppliers; and
•latent defects that may become apparent after a product has been released and even sold and used and that may result in recall and destruction of the product.
Any of these factors could result in delays or higher costs in connection with our clinical trials, regulatory submissions, required approvals, or commercialization of our products, which could expose us to liability or harm our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
We may not be able to obtain, afford, maintain, enforce, or protect our intellectual property rights covering our product candidates, including our autoimmune and inflammatory portfolio, and related technologies that are of sufficient type, breadth, and term throughout the world.
Our success with respect to our autoimmune and inflammatory portfolio and other product candidates will depend, in part, on our ability to protect patent and other intellectual property protections in both the U.S. and other countries, to preserve our trade secrets, and to prevent third parties from infringing on our proprietary rights. Our ability to prevent unauthorized or infringing use of our autoimmune and inflammatory portfolio and other product candidates by third parties depends in substantial part on our ability to leverage valid and enforceable patents and other intellectual property rights around the world.
The patent application process, also known as patent prosecution, is expensive and time-consuming, and we and our current or future licensors and licensees may not be able to prepare, file, and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner in all the countries that may be desirable. It is also possible that we or our current licensors and licensees, or any future licensors or licensees, will fail to identify patentable aspects of inventions made in the course of development and commercialization activities before it is too late to obtain patent protection by others on them. Therefore, these and any of our patents and applications may not be prosecuted and enforced in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. Moreover, our competitors independently may develop equivalent knowledge, methods, and know-how or discover workarounds to our patents that would not constitute infringement. Our partners or licensees may inappropriately take or use our intellectual property and/or confidential information to infringe our patents or otherwise violate their contractual obligations to us related to protection of our intellectual property. Any of these outcomes could impair our ability to enforce the exclusivity of our patents effectively, which may have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Due to constantly shifting global legal standards relating to patentability, validity, enforceability, and claim scope of patents covering pharmaceutical inventions, our ability to protect patents in any jurisdiction is uncertain and involves complex legal and factual questions, especially across countries. Accordingly, rights under any applicable patents that apply to us may not cover our product candidates or may not provide us with sufficient protection for our product candidates to afford a sustainable commercial advantage against competitive products or processes, including those from branded and generic pharmaceutical companies. In addition, we cannot guarantee that any patents or other intellectual property rights will issue from any pending or future patent or other similar applications related to us. Even if patents or other intellectual property rights have issued or will issue, we cannot guarantee that the claims of these patents and other rights are or will be held valid or enforceable by the courts or other legal authorities, through injunction or otherwise, or will provide us with any significant protection against competitive products or otherwise be commercially valuable to us in every country of commercial significance that we may target, or that a legislative or executive branch of government will not alter the rights and enforceability thereof at any time.
Competitors in the therapeutic areas of our strategic focus have created a substantial amount of prior art, including scientific publications, abstracts, posters, presentations, patents and patent applications, and other public disclosures, including on the Internet and various social media. Our ability to protect valid and enforceable patents and other intellectual property rights depends on whether the differences between our proprietary technology and the prior art allow our technology to be patentable over the prior art. We do not have outstanding issued patents covering all of the recent developments in our technology and are unsure of the patent protection that we will be successful in securing, if any. Even if the patents do issue successfully, third parties may design around or challenge the validity, enforceability, or scope of such issued patents or any other issued patents or intellectual property that apply to us, which may result in such patents and/or other intellectual property being narrowed, invalidated, or held unenforceable. If the breadth or strength of protection provided by the patents and other intellectual property we hold or pursue with respect to our product candidates is
challenged, regardless of our future success, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to develop, or threaten our ability to commercialize or finance, our product candidates.
The laws of some foreign jurisdictions do not provide intellectual property rights to the same extent or duration as in the U.S., and many companies have encountered significant difficulties in acquiring, maintaining, protecting, defending, and especially enforcing such rights in foreign jurisdictions. If we encounter such difficulties in protecting, or are otherwise precluded from effectively protecting, our intellectual property in foreign jurisdictions, our business prospects could be substantially harmed, especially internationally.
Patents have a limited lifespan. In the U.S., the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years after it is filed, with patent term extensions granted in certain instances to compensate for part of the period in which the drug was under development and could not be commercialized while under the patent. Without patent protection for our product portfolio, we may be open to competition from generic versions of these assets. BBI-02 is covered by a composition of matter patent issued in the U.S., Japan, China, and other key countries through at least 2038, subject to patent term extensions and adjustments that may be available depending on how this early-stage asset is developed, as well as a pending PCT application, and other foreign and U.S. applications for BBI-02, as of the date of this Quarterly Report. We are evaluating the patent protection and strategy for the remainder of the assets in-licensed from Voronoi and Carna.
Proprietary trade secrets and unpatented know-how and confidential information are also important to our business. Although we have taken steps to protect our trade secrets, unpatented know-how, and confidential information by entering into confidentiality and nondisclosure agreements with third parties and intellectual property protection agreements with officers, directors, employees, and certain consultants and advisors, there can be no assurance that binding agreements will not be breached or enforced by courts or other legal authorities, that we would have adequate remedies for any breach, including injunctive and other equitable relief, or that our trade secrets, unpatented know-how, and confidential information will not otherwise become known, be inadvertently disclosed by us or our agents and representatives, or be independently discovered by our competitors. If trade secrets are independently discovered, we would not be able to prevent their use, and if we and our agents or representatives inadvertently disclose trade secrets, unpatented know-how, and/or confidential information, we may not be allowed to retrieve the inadvertently disclosed trade secret, unpatented know-how, and/or confidential information and maintain the exclusivity we previously enjoyed.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights meaningfully throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting, and defending patents on our product candidates do not guarantee exclusivity. The requirements for patentability differ in certain countries, particularly developing countries, and can change over time in the same country. In addition, the laws of some other countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as laws in the U.S., especially when it comes to granting use and other kinds of patents and what kind of enforcement rights will be allowed, especially injunctive relief in a civil infringement proceeding. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in countries outside the U.S. and even in launching an identical version of our product notwithstanding our having a valid patent or other intellectual property rights in that country. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we, or our licensors or licensees, have not obtained patent or other protections to develop their own products, or produce copy products, and further, may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patent and other protections but enforcement against infringing activities is inadequate or where we have no patents or other intellectual property rights. These products may compete with our products, and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from commercialization or other uses.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of certain countries, particularly in developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents and other intellectual property protection, particularly those relating to
pharmaceuticals, and the judicial and government systems are often corrupt, apathetic, or ineffective, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our intellectual property rights generally. Proceedings to enforce our intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our global patents and other rights at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our global patent applications at risk of not issuing, and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuit that we initiate or infringement action brought against us, and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful when we are the plaintiff. When we are the defendant, we may be required to post large bonds to stay in the market while we defend ourselves from an infringement action.
In addition, certain countries in Europe and certain developing countries have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner may be compelled to grant licenses to third parties, especially if the patent owner does not enforce or use its patents over a protracted period of time. In some cases, the courts will force compulsory licenses on the patent holder even when finding the patentholder’s patents are valid if the court believes it is in the best interests of the country to have widespread access to an essential product covered by the patent. Further, there is no guarantee that any country will not adopt or impose compulsory licensing in the future. In these situations, the royalty the court requires to be paid by the license holder receiving the compulsory license may not be calculated at fair market value and can be inconsequential, thereby disaffecting the patentholder’s business. In these countries, we may have limited remedies if our patents are infringed or if we are compelled to grant a license to our patents to a third party, which could also materially diminish the value of those patents. This would limit our potential revenue opportunities. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we own or license, especially in comparison to what we enjoy from enforcing our intellectual property rights in the U.S. Finally, our ability to protect and enforce our intellectual property rights may be adversely affected by unforeseen changes in both U.S. and foreign intellectual property laws, or changes to the policies in various government agencies in these countries, including but not limited to the patent office issuing patents and the health agency issuing pharmaceutical product approvals. For example, in Brazil, pharmaceutical patents require prior initial approval from the Brazilian health agency, ANVISA. Finally, many countries have large backlogs in patent prosecution, and in some countries in Latin America, it can take years, even decades, just to get a pharmaceutical patent application reviewed notwithstanding the merits of the application.
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment, and other requirements imposed by governmental patent and similar agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for noncompliance with these requirements.
Periodic maintenance, validation, and annuity fees on any issued patent are due to be paid to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) and foreign patent agencies in several stages over the lifetime of a patent. The USPTO and various foreign governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment, and other similar provisions during the patent application process. While an inadvertent lapse can, in many cases, be cured by payment of a late fee or by other means in accordance with the applicable rules, there are situations in which noncompliance can result in abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction just for failure to know about and/or timely pay such fee. Noncompliance events that could result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application include failure to respond to official actions within prescribed time limits, non-payment of fees in prescribed time periods, and failure to properly legalize and submit formal documents in the format and style the country requires. If we or our licensors fail to maintain the patents and patent applications covering our product candidates for any reason, our competitors might be able to otherwise enter the market, which would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
In addition, countries continue to increase the fees that are charged to acquire, maintain, and enforce patents and other intellectual property rights, which may become prohibitive to initiate or continue paying in certain circumstances.
If we fail to comply with our obligations under our intellectual property and related license agreements, we could lose license rights that are important to our business. Additionally, these agreements may be subject to disagreement over contract interpretation, which could narrow the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or other key aspects of product development and/or commercialization, or increase our financial or other obligations to our licensors.
We have entered into in-license arrangements with respect to all of our product candidates. These license agreements impose various diligence, milestone, royalty, insurance, reporting, and other obligations on us. If we fail to comply with these obligations, the respective licensors may have the right to terminate or modify the license, or trigger other more disadvantageous contract clauses, in which event we may not be able to finance, develop or market the affected product candidate. The loss of such rights could expose us to liability and could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects.
Our commercial success depends on our ability to develop, manufacture, market, and sell our product candidates and use our proprietary technologies without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties and do this in one or more countries. We cannot assure that marketing and selling such product candidates and using such technologies will not infringe existing or future patents or other intellectual property rights. Numerous U.S. and foreign-issued patents and pending patent applications owned by third parties exist in the fields relating to our product candidates. As the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries expand and more patents and other intellectual property rights are issued, the risk increases that others may assert that our product candidates, technologies, or methods of delivery or use(s) infringe their patent or other intellectual property rights. Moreover, it is not always clear to industry participants, including us, which patents and other intellectual property rights cover various drugs, biologics, drug delivery systems and formulations, manufacturing processes, or their methods of use, and which of these patents may be valid and enforceable. Thus, because of the large number of patents issued and patent applications filed in our fields across many countries, there may be a risk that third parties may allege they have patent or other rights encompassing our product candidates, technologies, or methods.
In addition, there may be issued patents of third parties that are infringed or are alleged to be infringed by our product candidates or proprietary technologies notwithstanding the patents we may possess. Because some patent applications in the U.S. and other countries may be maintained in confidence until the patents are issued, because patent applications in the U.S. and many foreign jurisdictions are typically not published until eighteen (18) months or some other time after filing, and because publications in the scientific literature or other public disclosures often lag behind actual discoveries, we cannot be certain that others have not filed patent applications for technology covered by our patents or our pending applications. Our competitors may have filed, and may in the future file, patent applications covering our product candidates or technology similar to our technology. Any such patent application may have priority over our patent applications or patents, which could further require us to obtain rights to issued patents covering such technologies, which may mean paying significant licensing fees or royalties, or the like. If another party has filed a U.S. patent application on inventions similar to ours, we or the licensor may have to participate in the U.S. in an interference proceeding to determine priority of invention.
We may be exposed to, or threatened with, future litigation by third parties having patent or other intellectual property rights alleging that our product candidates or proprietary technologies infringe such third parties’ intellectual property rights, including litigation resulting from filing in the U.S. under Paragraph IV of the Hatch-Waxman Act or other countries’ laws similar to the Hatch-Waxman Act. These lawsuits could claim that there are existing patent rights for such drug, and this type of litigation can be costly and could adversely affect our operating results and divert the attention of managerial and technical personnel, even if we do not infringe
such patents or the patents asserted against us are ultimately established as invalid. There is a risk that a court or other legal authority would decide that we are infringing the third party’s patents and would order us to stop the activities covered by the patents. In addition, there is a risk that a court or other legal authority will order us to pay the other party significant damages for having violated the other party’s patents or intellectual property rights.
Because we rely on certain third-party licensors, licensees, and partners and will continue to do so in the future, around the world, if one of our licensors, licensees, or partners is sued for infringing a third party’s intellectual property rights, this could expose us to liability, and our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects could suffer in the same manner as if we were sued directly. In addition to facing litigation risks, we have agreed to indemnify certain third-party licensors, licensees, and partners against claims of infringement caused by our proprietary technologies, and we have entered or may enter into cost-sharing agreements with some of our licensors, licensees, and partners that could require us to pay some of the costs of patent or other intellectual property rights litigation brought against those third parties whether or not the alleged infringement is caused by our proprietary technologies. In certain instances, these cost-sharing agreements could also require us to assume greater responsibility for infringement damages than would be assumed just on the basis of our technology.
The occurrence of any of the foregoing could expose us to liability or adversely affect our business, financial condition, operating results, and prospects at any time.
General Risk Factors
Provisions of Delaware law and our restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may discourage another company from acquiring us and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Provisions of Delaware law and our restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may discourage, delay, or prevent a merger or acquisition that our stockholders may consider favorable, including transactions in which you might otherwise receive a premium for your shares. In addition, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace or remove our board of directors. These provisions include, but are not limited to:
•authorizing the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock without any need for action by stockholders;
•providing for a classified board of directors with staggered terms;
•requiring supermajority stockholder voting to effect certain amendments to our current certificate of incorporation and bylaws;
•eliminating the ability of stockholders to call special meetings of stockholders; and
•establishing advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted on by stockholders at stockholder meetings.
Although we believe these provisions collectively provide for an opportunity to receive higher bids by requiring potential acquirers to negotiate with our board of directors, they would apply even if an offer may be considered beneficial by some stockholders. In addition, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors, which is responsible for appointing the members of our management.
If we fail to attract and retain management and other key personnel and directors, we may be unable to continue to successfully develop or commercialize our product candidates or otherwise implement our business plan.
Our ability to compete in the highly competitive pharmaceuticals industry depends on our ability to attract and retain highly qualified managerial, scientific, medical, legal, regulatory and compliance, sales and marketing, business development, commercial and other personnel, and directors of our board of directors. We are highly dependent on our management, scientific personnel, and directors. The loss of the services of any of these individuals could impede, delay, or prevent the successful development of our product pipeline, completion of our current or planned clinical trials, commercialization of our product candidates, or in-licensing or acquisition of new assets and could impact negatively our ability to implement successfully our business plan in a way that complies with all applicable laws. If we lose the services of any of these individuals, we might not be able to find suitable diverse replacements on a timely basis or at all, and our business could be harmed as a result. We might not be able to attract or retain diverse qualified management and other key personnel or directors in the future due to the intense competition for qualified individuals among biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and other businesses. This risk is heightened recently for most employers by the global reaction to the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on worker availability and government regulation of workplace practices associated with public health and other factors.
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS
None.
ITEM 3. DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES
Not applicable.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
ITEM 6. EXHIBITS
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exhibit
Number | | Description of Exhibit | Form | Date of Filing | Exhibit Number | Filed Herewith | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| 3.1 | | | | | | × | | | |
| 3.2 | | | | | | × | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| 10.1† | | | 8-K | 5/3/2022 | 10.1 | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| 10.2† | | | 8-K | 5/3/2022 | 10.2 | | | | |
| 10.3† | | | 8-K | 5/3/2022 | 10.3 | | | | |
| 10.4+ | | | 8-K | 5/17/2022 | 10.1 | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| 10.5 | | | 8-K | 5/25/2022 | 10.1 | | | | |
| 31.1 | | | | | | × | | | |
| 31.2 | | | | | | × | | | |
| 32.1* | | | | | | × | | | |
| 101.INS | | Inline XBRL Instance Document | | | | × | | | |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | | | | × | | | |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | | | | × | | | |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | | | | × | | | |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | | | | × | | | |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | | | | × | | | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101) | | | | × | | | |
__________________
| | | | | |
| + | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan. |
| |
| † | Certain confidential information contained in this agreement has been omitted because it (i) is not material and (ii) would be competitively harmful if publicly disclosed. |
| * | This certification is being furnished pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 and is not being filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act and is not to be incorporated by reference into any filing of the Registrant, whether made before or after the date hereof. |
| |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Quarterly Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Brickell Biotech, Inc. |
| | | | |
| Date: August 11, 2022 | | By: | | /s/ Robert. B. Brown |
| | | | Robert B. Brown Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
| | | | |
| | By: | | /s/ Albert N. Marchio, II |
| | | | Albert N. Marchio, II Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |